23 Dec 2016
Name: Ascorbic acid
The Latin name of the substance Glutathione
Acidum ascorbinicum (genus. Acidi ascorbinici)
Chemical name: L-Ascorbic acid
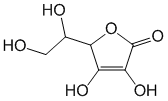
Formula - C6H8O6
Therapeutic substances Ascorbic acid - Vitamins and vitamin-like agent
The nosological classification (ICD-10)
B15 Acute hepatitis A
B83.9 Unspecified Helminthiases
B99 Other infectious diseases
D68.9 Bleeding disorders, unspecified
D69.9 Hemorrhagic condition, unspecified
D74.9 Unspecified Methaemoglobinemia
E54 Lack of ascorbic acid [vitamin C]
E83.1 Disorders of iron metabolism
F05.9 Delirium, unspecified
F10.4 abstinent state with delirium
G71.0 Muscular dystrophy
I61 Intracerebral haemorrhage
I999 Diagnosis of diseases of the circulatory system
K25 Gastric ulcer
K26 Duodenal Ulcer
K31.8.1 Achilios stomach
K52 Other noninfectious gastroenteritis and colitis
K73.9 Chronic hepatitis, unspecified
K74.6 Other and unspecified cirrhosis of liver
K81.9Cholecystitis, unspecified
L40.9Psoriasis, unspecified
L53.9 Erythematous condition, unspecified
L81.4 Other melanin hyperpigmentation
L98.4 Chronic ulcer of skin, not elsewhere classified
N76 Other inflammatory diseases of the vagina and vulva
N93.9 Abnormal uterine and vaginal bleeding, unspecified
O26.9 condition associated with pregnancy, unspecified
R04.0 Epistaxis
R04.8.0 Bleeding pulmonary
T14.2 Fracture of unspecified body in the field of
T30 thermal and chemical burns, unspecified
T45.4 Poisoning by iron and its compounds
T66 Unspecified effects of radiation
T80.9 Complications associated with infusion, transfusion and therapeutic injection, unspecified
Z39.1 Help and inspection nursing mother
Z54 recovery period
CAS code - 50-81-7
Characteristics substance Ascorbic acid
Vitamins (Vitamin C). Ascorbic acid - a white crystalline powder sour taste. Easily soluble in water (1: 3.5), slowly soluble in ethanol (1:30), absolute ethanol (1:50), glycerol (1: 100), propylene glycol (1:20). Solubility in water: 80.0% at 100 ° C; 40.0% at 45 ° C. Practically insoluble in ether, benzene, chloroform, petroleum ether, oils, fats. Under the influence of air and light gradually darkens. The dry form is stable in air, water solutions rapidly oxidize in air. The molecular weight of 176.13.
Sodium ascorbate - fine crystals, freely soluble in water: 62 g / 100 ml at 25 ° C, 78 g / 100 ml at 75 ° C.
Most primates (including humans), guinea pigs, some birds, fish can not synthesize vitamin C in the human body the necessary reserve is replenished by receipts from food.
For medical purposes, ascorbic acid is produced synthetically.
Pharmacology
Mode of action - complementary deficiency of Vitamin the C, metabolic regulating redox processes, antioxidant.
It has strong antioxidant properties. Regulates H + transport in many biochemical reactions, improves glucose utilization in the cycle of tricarboxylic acids involved in the formation of tetrahydrofolic acid and tissue regeneration, the synthesis of steroid hormones, collagen, procollagen, carnitine, hydroxylation of serotonin. It supports the colloidal state of the intercellular substance and normal capillary permeability (inhibits hyaluronidase). It activates the proteolytic enzymes involved in the metabolism of aromatic amino acids, pigments and cholesterol promotes the accumulation of glycogen in the liver. By activating the respiratory enzymes in the liver increases its detoxification and protein function, increases the synthesis of prothrombin. It improves bile secretion, restores the function of pancreatic exocrine and endocrine - thyroid. Regulates the immunological reaction (activates the synthesis of antibodies, C3 component of complement, interferon), promotes phagocytosis, increases the body's resistance to infection. It has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect. It stops the release of histamine and accelerates degradation, inhibits the formation of PG and other mediators of inflammation, and anaphylaxis. It reduces the need for vitamins B1, B2, A, E, folic acid, pantothenic acid. ascorbic acid deficiency leads to the development of hypovitaminosis, in severe cases - vitamin deficiency (scurvy, scurvy).
Absorbed in the small intestine (duodenum, in part - in the ileum). With increasing doses up to 200 mg is absorbed to 70%; with further increase the absorption of the dose is reduced (50-20%). The pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, constipation, diarrhea), worm infestation, giardiasis, consumption of fresh fruit and vegetable juice, alkaline drinking - reduced utilization of ascorbate in the intestine. Cmax after oral administration is achieved after 4 hours. The degree of binding to plasma proteins is low (about 25%). Easily penetrates the leukocytes, platelets, and then - in all the tissues; the largest concentrations are found in the glandular tissue. Deposited in the posterior pituitary, adrenal cortex, ocular epithelia, intermediate cells testes, ovary, liver, brain, spleen, pancreas, lung, kidney, intestinal wall, heart, muscle, thyroid gland. It passes through the placenta. Metabolized primarily in the liver, and more in dezoksiaskorbinovuyu and diketogulonovuyu oxaloacetic acid. Unchanged ascorbate and metabolites excreted in the urine, faeces, sweat, breast milk. Displayed in hemodialysis.
At high doses, where the plasma concentration reaches more than 1.4 mg / dl, excretion increases sharply, the increased excretion may persist after discontinuation. Smoking and the use of ethyl alcohol accelerates the destruction (transformation into inactive metabolites), sharply reducing inventories in the body.
When used in the form of vaginal tablets Vaginal ascorbic acid reduces the pH, inhibit bacterial growth, and helps to restore and maintain normal levels of vaginal flora and pH (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus gasseri). Thus, at lower pH in the vagina for several days it occurs pronounced inhibition of growth of anaerobic bacteria, as well as the restoration of normal flora.
Application of the substance Ascorbic acid
Hypovitaminosis C, hemorrhagic diathesis, kapillyarotoksikoz, hemorrhagic stroke, hemorrhage (including nasal, pulmonary, uterine), infectious disease, idiopathic methemoglobinemia, intoxication, including chronic intoxication iron preparations, alcoholic and infectious delirium, acute radiation sickness, post-transfusion complications, liver diseases (Botkin's disease, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis), gastrointestinal disorders (Akhil, peptic ulcer disease, especially after bleeding, enteritis, colitis), helminth infections, cholecystitis, adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), sluggish healing wounds, ulcers, burns, broken bones, dystrophy, physical and mental overload, the period of convalescence after an illness, pregnancy (especially prolific, against nicotine or drug dependence), lactation, hemosiderosis, melasma, erythroderma, psoriasis, chronic common dermatoses. In laboratory practice - for labeling of red blood cells (together with sodium chromate 51Cr). You can buy online - Vitamin C ascorbic acid injection.
Vaginal Tablets - chronic or recurrent vaginitis due to anaerobic flora (due to changes in pH of the vagina); normalization of disturbed vaginal microflora.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, thrombophlebitis, tendency to thrombosis, vulvovaginal candidiasis (for Tables. Vaginal).
Restrictions for application
Diabetes, deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, hemochromatosis, sideroblastic anemia, thalassemia, hyperoxaluria, oxalosis, urolithiasis.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
The minimum daily need in ascorbic acid in II-III trimesters of pregnancy - about 60 mg. It should be borne in mind that the fruit can adapt to high doses of ascorbic acid, which is taken by pregnant women, and then the newborn may develop withdrawal symptoms. It has been reported that treatment with high doses of vitamin C during pregnancy, is associated with the risk of scurvy in infants with a / in the introduction of high doses - the threat of termination of pregnancy due estrogenemii (Nonteratogenic effects).
The minimum daily requirement for lactation - 80 mg. maternal diet containing adequate amount of ascorbic acid sufficient for preventing an infant deficiency. Theoretically, there is a danger for the child's mother in the application of high doses of ascorbic acid (nursing mothers are advised not to exceed the daily requirement of ascorbic acid).
For injectable forms. Animal reproduction studies using ascorbic acid injection is not carried out. It is not known whether vitamin C can be injected, while pregnant women have embryotoxic action or violate the reproductive ability. The injectable form can be administered during pregnancy only if absolutely necessary.
Side effects of Ascorbic acid substance
Cardio-vascular system and blood (blood, hemostasis): thrombocytosis, giperprotrombinemiya, erythropenia, leukocytosis.
From the nervous system and sensory organs: the excessively rapid on / in the introduction - dizziness, weakness.
From the digestive tract: ingestion - irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), diarrhea (when receiving doses greater than 1 g / day), damage to the tooth enamel (with intensive use of chewable tablets or oral forms of resorption).
From a metabolism: metabolic inhibition of glycogen synthesis, excessive formation of corticosteroids, sodium and water retention, hypokalemia.
With the genitourinary system: an increase in urine output, renal glomerular damage the machine, the formation of calcium oxalate urinary stones (especially chronic administration at doses greater than 1 g / day).
Allergic reactions: skin rash, skin redness.
Other: pain at the injection site (with the / m introduction). For vaginal tablets: local reactions - burning or itching of the vagina, increased mucous secretions, redness, swelling of the vulva.
Interaction
Increasing the concentration of salicylates in the blood (increased risk of crystalluria), ethinyl estradiol, penicillin and tetracycline, reduces - oral contraceptives. Aspirin, oral contraceptives, fresh juices and alkaline water reduces the absorption and assimilation. It increases the activity of norepinephrine. It reduces the anticoagulant effect of coumarin derivatives, heparin. It improves the intestinal absorption of iron (due to the transfer of ferric to ferrous). In an application with deferoxamine may increase tissue iron toxicity, including and cardiac heart failure. It increases total clearance of ethanol. It may affect the efficiency of disulfiram for the treatment of chronic alcoholism. Quinoline series of preparations, calcium chloride, salicylates, corticosteroids, long-term use deplete vitamin C. A solution of ascorbic acid when mixed in the same syringe enters into chemical reaction with many drugs.
OverdoseSymptoms: long-term use of high doses (more than 1 g) - headache, increased CNS excitability, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperacid gastritis, gastric ulceration gastrointestinal mucosa, depression insular pancreatic apparatus function (hyperglycemia, glucosuria), hyperoxaluria, nephrolithiasis (calcium oxalate), damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, moderate pollakiuria (when receiving doses of 600 mg / day).
Reducing capillary permeability (possible deterioration of the trophic tissue, increased blood pressure, hypercoagulation, the development of microvascular complications).
The on / in the introduction of high doses - the threat of termination of pregnancy (due estrogenemii), hemolysis.
Dosing and Administration of Ascorbic acid
Inside, in / m, / in, vaginally. Inside, after a meal. As a preventive measure (in the winter-spring period and malnutrition): adults - 50-100 mg / day (children - 25-75 mg / day) during pregnancy and lactation - 300 mg / day for 10-15 days further - 100 mg / day. For therapeutic purposes: adults - 50-100 mg 3-5 times a day (children - 50-100 mg 2-3 times a day). V / m and / in 5-10% solution - 1.5 ml for poisoning - 3 g (60 ml). Timing of treatment depend on the nature and course of the disease. Intravaginal - 1 vaginal tablet inserted into the vagina before going to bed, course of treatment - 6 days, can repeat courses.
Precautions for Ascorbic acid substance
In appointing the solutions I / O to avoid too rapid of their introduction. During long-term therapy should be monitored for renal function, blood pressure and glucose levels (especially at high doses). With special care prescribe high doses to patients with urolithiasis, diabetes, propensity to thrombosis, receiving anticoagulant therapy, are on a salt-free diet.
Ascorbic acid as a reducing agent, may distort the results of the various laboratory tests (glucose content in the blood of bilirubin, transaminases, LDH, glucose in the urine, including determining the false-negative results of a study of stool for occult blood).
When used in the form of vaginal tablets, ascorbic acid does not inhibit the growth of fungal vaginal flora. Such manifestations as burning and itching can be caused by the presence of concomitant asymptomatic fungal infection, so when these symptoms should be reviewed to avoid fungal infection. Breaks in applying vaginal tablets in connection with inter-cyclic or menstrual bleeding is not required.
Trading names of drugs with Ascorbic acid working substance
Trade Name Index
Additives Vitamin C
Asvitol
Askovit
Askorbinka ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
Ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
Ascorbic acid bufus
Ascorbic acid and sugar
Ascorbic acid-Vial
Ascorbic acid-Rusfar
Ascorbic acid-UBF
Ascorbic acid 0.05 g dragees
Ascorbic acid injection 10%
Ascorbic acid injection 5%
Ascorbic acid tablets 0.025 g
Ascorbic acid tablets 0.05g
Vaginorm C
Vitamin C
VITAMIN C PLUS Kid's formula Farmamed
Vitamin C-Inektopas
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
Multi-tabs® with Vitamin C
With Pliva
Rostvit
Setebe 500
Cevikap
Celaskon® Vitamin C
Celaskon® effect of Vitamin C
Celaskon® Effervestsens

 Cart
Cart