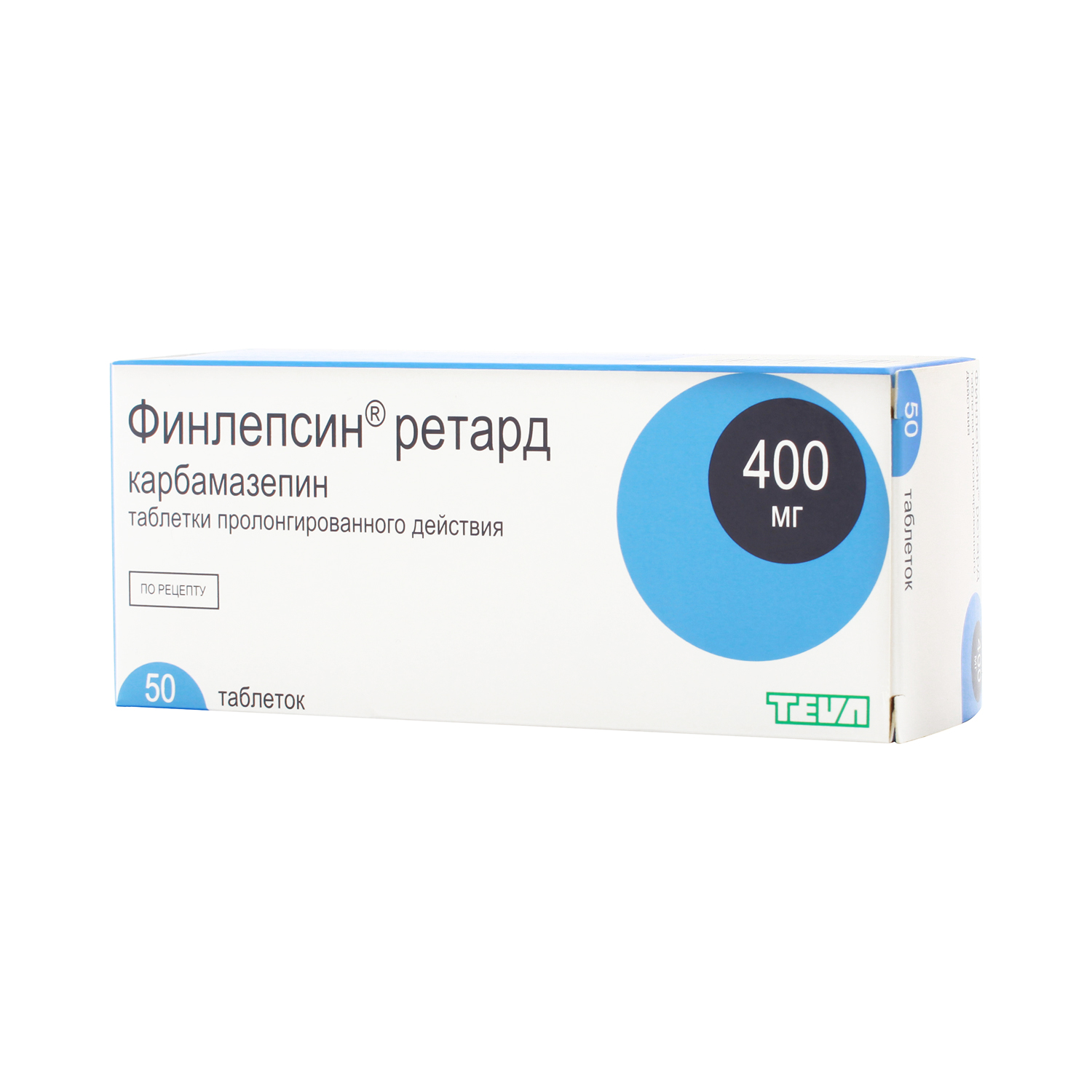
Finlepsin - instructions, dosage, side effects, analogs
20 Jan 2020
Antidepressant: Finlepsin
Active ingredient: Carbamazepine (carbamazepine)
Analogs: Actinerval, Apo-Carbamazepine, Gene-Karpaz, Zagretol, Zeptol, Carbadac, Carbaleptin retard, Carbamazepine, Carbamazepine Nycomed, Carbamazepine Rivo, Carbamazepine-ACRI, Carbamazepine-Teva, Carbamazepine-Pharmacia-AD, Carbamazepine-Ferein, Carbapine, Carbasan, Carbatol , Karzepin-200, Mazepin, Novo-Karbamaz, Stazepin, Storilat, Tegretol, Tegretol CR, Timonil, Finzepin, Finlepsin 200 retard, Finlepsin 400 retard, Finlepsin retard, Epial.
"Finlepsin" is an antiepileptic drug, has antipsychotic and antimanic effects, and also acts as an analgesic for neurogenic pain. The drug begins to act fairly quickly: the anticonvulsant effect, as a rule, manifests itself in the interval from several hours to several days. Antimanic (the same antipsychotic) same effect occurs after 7-10 days after the start of the application of "Finlepsin".
The drug is effective both in monotherapy (by 70-85%), and in combination with valproate (another drug of the first choice). In addition to the antiepileptic itself, it has a good effect on cognitive and psychoemotional functions. The transition to monotherapy with a prolonged form of the drug called "Finlepsin retard" makes it possible to prevent dangerous psychotic post-prandial behavior, which was manifested by the therapy with other drugs of similar effect.
"Finlepsin" is effective for treating patients with behavioral disorders of non-epileptic origin (also paroxysmal), for example, with hyperactivity and children's attention deficit syndrome. With the correct selection of dosages (usually low doses in the amount of 300-400 mg / day) after a 2-6 month course, there are significant improvements in behavior and adaptation to school.
Clinical studies of the possibilities of "Finlepsin" illustrate its high effectiveness in the fight against epileptic attacks. Thus, positive changes in the condition were noted in 96% of patients, while a significant reduction in the seizures (by 75-100%) was recorded in 43% of patients, and a significant (by 50-75%) - in 35% of the subjects.
Indications for use:
- epilepsy (both complex and simple symptomatology of partial seizures), tonic-clonic convulsions (usually focal genesis: diffuse large seizures and large seizures in sleep), epilepsy in mixed forms;
- neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve (including and with spasms of the facial muscles);
- neuralgia idiopathic glossopharyngeal;
- consequences of diabetes (pain associated with peripheral nerve damage, as well as pain caused by diabetic neuropathy);
- seizures on the background of multiple sclerosis, movement and speech disorders in the form of seizures, paroxysmal pain attacks and paresthesia;
- alcohol withdrawal syndrome (with concomitant symptoms: sleep disorders, anxiety, convulsions, increased excitability);
- various psychotic disorders (malfunctions in the limbic system, affective, and schizoaffective disorders);
- psychoses (primarily manic-depressive psychosis, hypochondriacal and anxious-agitated depression, excitation of a catatonic character).
Contraindications: People with hypersensitivity (including tricyclic compounds), atrioventricular blockade, disorders of bone marrow hematopoiesis (eg, anemia, leukopenia), intermittent acute porphyria (also in the anamnesis), with simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors or lithium preparations. In addition, it is forbidden to take the drug for children under 6 years (this refers to the variety "Finlepsin retard").
Dosage and administration: "Finlepsin" is taken orally, washed down with liquid, during or after a meal. The dose range, as a rule, is 400 -1200 mg / day, exceeding the daily dose of 1600 mg / day is not recommended because of the possible appearance (or intensification) of side effects.
The initial dosage for adults with anticonvulsant treatment corresponds to 200-400 mg of the drug per day (1-2 tablets). Gradually, it is increased to maintenance (4-6 tablets or 800 - 1200 mg / day).
Treatment is of a long-term nature and lasts until 2-3 years, free of seizures, have passed.
Refusal of finlepsin: From "Finlepsin" they refuse gradually, reducing the dose for 1-2 years.
Dosage for children: 1 to 5 years: the initial dose is 1/4 tablets 1-2 times a day, supporting - 1 tablet 1-2 times a day.
Up to 4 years, as a rule, treatment starts with a dosage of 20-60 mg / day, increasing it by 20 to 60 mg / day every other day until a maintenance dose is reached. Children older than 4 years can start taking "Finlepsin" with 100 mg / day and increase the dose every other day for 100 mg / day to the maintenance dose.
From 6 to 10 years: the initial - 1/2 tablet 2 times a day, supporting - 1 tablet "Finlepsin" 3 times a day.
From 11 to 15 years: the initial dose - 1/2 tablet of the drug 2-3 times a day, supporting - 1 tablet 3-5 times a day.
Therapy of trigeminal neuralgia, genuinous glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Initial dose: 400-600 mg / day (2-3 tablets). It gradually increases until the pain disappears completely, the maintenance dose is 400-800 mg / day (2-4 tablets). It is advisable to break the dose into two doses. For elderly patients it makes sense to choose the lowest limit of the initial dosage.
The course of treatment is several weeks. Lowering the dose, find out whether there is an opportunity to return pain. If the pain manifests itself again, continue the treatment (maintenance dose).
Painful sensations in diabetic neuropathy: The average daily dose equals 600 mg of the drug (3 tablets). If absolutely necessary, it can be increased to a dose of 1200 mg / day (6 tablets). To consume in three steps. Duration of treatment is several weeks.
Multiple sclerosis with epileptiform cramps: Twice a day, 1-2 tablets twice a day (or 400-800 mg). The duration of treatment, as a rule, is several weeks.
Prevention and treatment of various psychoses: The initial dose in most cases coincides with the supporting (1-2 tablets or 200 - 400 mg / day). If necessary, it can be increased to 800 mg / day (2 tablets twice a day).
Side effects: The most common side effects are: drowsiness, dizziness, general weakness, ataxia, headache, leukopenia, nausea, fluid retention, vomiting, dry mouth.
Storage conditions: Store up to the expiration date in a dry place inaccessible to children, under temperature conditions not exceeding 30 ° C.

 Cart
Cart