Review of Psilocybes
14 Aug 2018
Currently, the genus psilocybe has about 20 species. At the same time, American and Asian species are poorly studied. Species of this genus are cosmopolitan and widely distributed in almost all continents. Fungi of the genus psilocybe are saprophytes. They settle on soil, dead branches and stems of plants, are found on sawdust, many live on sphagnum marshes, peat, manure. Occur in the forest on humus forest. A characteristic feature of many fungi is dwelling on boggy soil. Therefore they belong to the helophytic species.
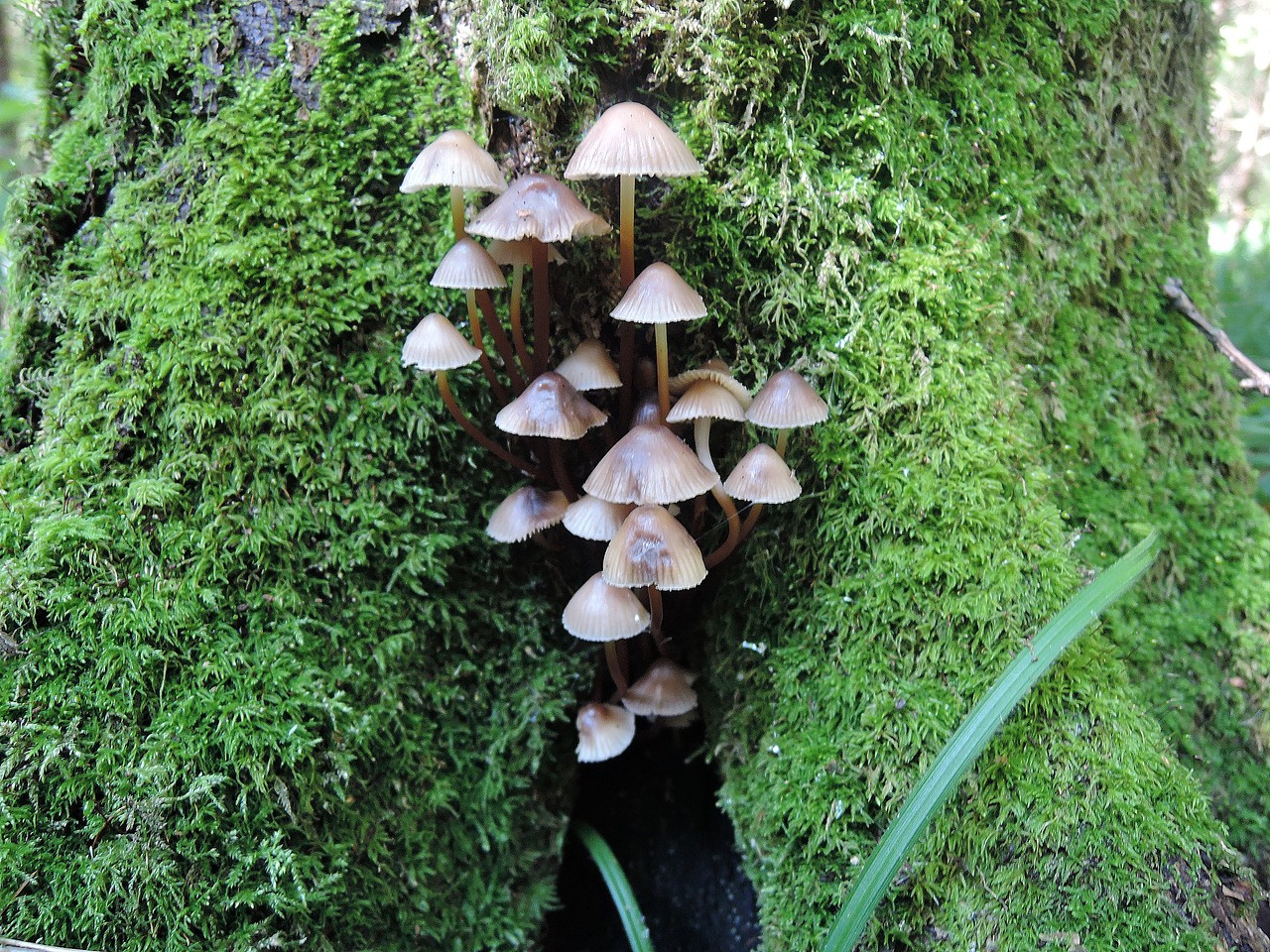

The color of the bonnet is reddish, yellow or olive. The cap is dry or watery, depending on the habitat of the fungus. Plates accreted to the stem or slightly descending along it. The spores are brown-violet, ellipsoidal or grain-shaped. Bedspread is barely noticeable or completely absent. The foot is cartilaginous.
There are no edible mushrooms in this way. However, they have a peculiar application. In some manuscripts of the 16th - 17th centuries, in which the disappearing culture of the Aztecs is described, there is a mention of Indian ritual ceremonies, in connection with which mushrooms that caused hallucinations were used. The hallucinogenic properties of some fungi were known to the Maya priests in ancient Mexico, who used them in religious ceremonies. These mushrooms have been used in Central America for a very long time. The Indians consider them divine mushrooms. Found even stone images of mushrooms, revered by Indians as deities.
Of the fungi belonging to the genus psilocybe, a hallucinogenic substance called psilocybin was isolated. This is a 4-oxidimethyl-tryptamine phosphate ester (CH12O4N2P). Pharmacological tests have shown that one hundred psilocybin is not toxic. A dose of about 1 mg causes a person intoxicated within 20 to 30 minutes after ingestion. A dose of up to 4 mg causes a state of detachment from reality, and at higher doses (up to 12 mg) profound changes in the psyche occur, hallucinations occur. Currently, this substance is synthesized abroad and used to treat certain mental illnesses. Very interesting is the effect of psilocybin on patients suffering from memory loss. Almost 50% of patients have memories, revival, fear and restraint disappear. Patients remember what they have forgotten, and help doctors to better understand the causes of the disease. However, the substance of psilocybin becomes a very dangerous hallucinogenic drug if it is used not for medical purposes, without medical supervision.
To date, psilocybin has been found in some fungi from the genus Paneeolus (Panaeolus), Stropharia (Stropharia), Anellaria (Anellaria). To the hallucinogenic fungus is now attributed to about 25 species and 75% of them are members of the psilocybe family (Psilocybe), for example P. caerulescens, P. semilanceata, P. pelliculosa, P. cubensis.
In addition to psilocybin, hallucinogenic fungi also have another substance that also has a psychotropic effect: psilocin, close in structure to psilocybin. In the fungi of the genus stropharia and psilocybe, as well as in the genus Paneolus, indole derivatives (tryptamine, etc.), which have an anticoagulant effect on solutions of fibrinogen, have been found. Fungal preparations with this effect can be used in the treatment of thromboses.
The species growing on wet, swampy places and being there usual are the dark-brown psilocybe (P. atrobrunnea) with a bell-shaped watery cap of 3-5 cm in diameter. The plates, adhering to the foot, later lagging behind it, are rare, thick, brownish -series, with a white edge. Taste and smell of carbohydrates or flour. A mushroom grows among sphagnum mosses.
On the same peat bogs and boggy meadows, in forests among mosses is widespread psilotsibe moist (P. paupera). It is a small mushroom with an outstretched reddish-brown cap with a diameter of 1.5-3 cm, which has a more prominent, rounded tubercle of a darker color on top. The plates, attached to the stem, are grayish-violet. Leg is hollow inside, rusty-brown, above light, fibrous.
On the pastures and in the hummocks there is a heathlope psyche (P. ericaceae). The cap of this fungus is convex or campanulate, in the center depressed, 2-4 cm in diameter, brown or dark brown with a yellow hue, slightly mucous, with white flakes on the edge. The plates, attached to the stem, are wide, swollen, tapering to the ends and with a white edge. Their color is yellowish-brown, then almost black.
Psilocybe coprophilia (P. coprophila) - a typical coprophilic fungus, settling on cow dung, on pastures. The hat is outstretched, with a tubercle, 2-4 cm in diameter, reddish-brown, smooth, weakly lingual. Flesh white, thin. The plates are notorious, slightly protruding along the stem, very wide, frequent, bluish-gray, later darkening. Leg slightly thickened below, pale, powdery at the top.
In forests, pastures and along the outskirts of the roads, there is also a hallucinogenic fungus with a very characteristic structure - the psilocybe is semi-lanceolate (P. semilanceata). The hat is conical, then weakly prostrated, with a sharp tuber, 1-5 cm in diameter, yellowish-greenish, then darkening, brownish, with a peeling cut off in the form of mucous membranes. The plates are narrow, adherent to the stalk, frequent, at first light cream, and on maturation dark purple-violet.

 Cart
Cart