Diazepam - Active Substances. Instruction and Application, Dosage
26 Dec 2016
Name: Diazepam
The Latin name of the substance Diazepam
Diazepamum (genus. Diazepami)
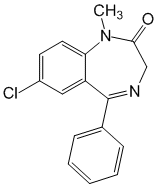
chemical name 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-on
Formula - C16H13ClN2O
Therapeutic agents of Diazepam:
Drugs affecting neuromuscular transmission
Anxiolytics
Antiepileptics
The nosological classification (ICD-10)
F05 Delirium, not induced by alcohol or other psychoactive substances
F06 Other mental disorders due to brain damage and dysfunction and to physical disease
F06.4 Organic anxiety disorder
F10.2 alcohol dependence syndrome
F10.3 abstinence
F10.4 abstinent state with delirium
F10.5Alcoholic psychosis
F11 Mental and behavioral disorders due to use of opioids
F20 Schizophrenia
F29 Unspecified Inorganic psychosis
F32 Depressive episode
F34.1 Dysthymia
F40.0 Agoraphobia
F40.2 Specific (isolated) phobias
F41.0 Panic disorder [episodic paroxysmal anxiety]
F43.0 Acute stress reaction
F43.1 Post-traumatic stress disorder
F43.2 Disorder adaptive reactions
F44 Dissociative [conversion] disorders
F45 Somatoform disorders
F51.0 Insomnia inorganic etiology
F60 Specific personality disorders
F63 Disorders of habit and impulse
F95 Tiki
G40 Epilepsy
G41 Status epilepticus
G47.0 Disorders of falling asleep and maintaining sleep [insomnia]
G83.9 Paralytic syndrome, unspecified
L29 Itching
L30.9 Dermatitis, unspecified
M13.0 Polyarthritis, unspecified
M13.9 Arthritis, unspecified
M60 Myositis
M62.4 Contracture of muscle
M71 Other bursopathies
N94.3 syndrome premenstrual tension
N95.1 menopausal and menopausal status of women
O15 Eclampsia
O62.9 Violation of labor, unspecified
R25.2 Cramp and spasm
R25.8.0 hyperkinesia
R32 Urinary incontinence unspecified
R45.1 Restlessness and agitation
R45.4 Irritability and anger
R45.7 State of emotional shock and stress, unspecified
R51 Headache
T14.9 Injury, unspecified
Z100 * CLASS XXII Surgical practice
CAS code - 439-14-5
Characteristics substance Diazepam
Anxiolytic, benzodiazepine derivative.
White or white with a slight yellowish tint, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 284.74. Practically insoluble in water, it is soluble in alcohol, insoluble in chloroform.
Pharmacology
Mode of action - anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, central, sedative, hypnotic.
It interacts with specific benzodiazepine receptors located in the postsynaptic GABAA receptor complex in the brain's limbic system, thalamus, hypothalamus, ascending activating reticular formation of the brain stem and neurons of lateral horns of the spinal cord. It increases the sensitivity of GABA receptors to neurotransmitter (GABA) that causes the increase in the frequency of opening the channels in the plasma membrane of neurons to incoming currents chlorine ions. The result is increased inhibitory effects of GABA interneurons and inhibition of transfer in the CNS.
The anxiolytic activity is shown the ability to stop internal anxiety, fear, anxiety, stress. It has anti-panic and amnestic (predominantly with parenteral use) action.
In the treatment of sleep disorders diazepam use as a hypnotic expedient in those cases where it is desirable to simultaneously get anxiolytic action during the day. You can also like Cerluten.
Central muscle relaxant effect is due to inhibition of polysynaptic spinal reflexes.
It has a pronounced anticonvulsant effect is applied for the treatment of epilepsy convulsions, mental equivalents for edema epileptic status.
In acute alcohol withdrawal eases symptoms such as agitation, nervousness, restlessness, anxiety, tremors, and also reduces the likelihood of developing or signs emerged of acute delirium, including hallucinations.
Effective in a parenteral administration in adults in acute conditions involving psychomotor agitation, convulsions and other.
Sedation occurs several minutes after the on / in the introduction and in 30-40 minutes after i / m. After removal of the acute manifestations of the disease diazepam appointed interior.
In practice anesthetics used to reduce fear, anxiety, stress and reduce the acute stress response in the preoperative period and complex, including diagnostic, intervention in therapy and surgery. In the latter case, it may weaken memories of the patient of the procedure (cardioversion, cardiac catheterization, endoscopic procedures, reduction of dislocation and repositioning bone fragments, biopsies, dressing burn wounds, etc.).
Diazepam enhances the effectiveness of induction of anesthesia (premedication with diazepam may decrease the dose of fentanyl required to cause effect at induction of anesthesia, and reduce the time to turn off the mind with the help of induction doses).
Increases pain threshold, has antiarrhythmic effect, lowers blood pressure (with the rapid on / in the introduction). It reduces nocturnal gastric acid secretion. It has the ability to impede the outflow of intraocular fluid or increase its secretion and, thus, increase intraocular pressure.
In experimental studies have shown that diazepam LD50 ingestion of 720 mg / kg (mouse) and 1240 mg / kg (rats).
reproduction study in rats receiving diazepam at doses of 1, 10, 80 and 100 mg / kg orally for 60-228 days prior to hybridization showed that at doses of 100 mg / kg was observed decrease in the number of pregnancies and offspring survival (possibly due to sedation action, resulting in a decrease of interest in mating and rearing of offspring). Doses less than 100 mg / kg had no effect on neonatal survival.
A study in rabbits when receiving diazepam at doses of 1, 2, 5 and 8 mg / kg with the 6 th to the 18 th day of pregnancy showed no adverse effects on reproduction and teratogenicity.
Once inside quickly and well (about 75% of the dose) is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After the / m of absorbed completely, but more slowly than when taken orally (the rate of absorption depends on the site of administration, greatest - when injected into the deltoid muscle). Rectal administration of diazepam solution is rapidly absorbed. Cmax in the blood is reached after 0.5-2 hours (when taken orally), 0.5-1.5 hours (with the / m introduction). The equilibrium concentration in the blood is achieved with daily intake after 5 days - 2 weeks. Treated biotransformation (diazepam 98-99%) in the liver with the formation of pharmacologically active metabolites: dezmetildiazepama (nordiazepama), oxazepam and temazepam. Diazepam and its active metabolites bind to plasma proteins (diazepam 98%), pass through the blood-brain barrier, the placenta, into breast milk (found at a concentration of 1/10 of the maternal plasma concentrations in breast milk). Diazepam volume of distribution at steady state of 0.8-1.0 l / kg. Period poluraspredeleniya diazepam -. To 3.2 hours T1 / 2 in adults is 20-70 hours (diazepam), 30-100 hours (nordiazepam) 9,5-12,4 (temazepam), 5-15 hours (oxazepam) . T1 / 2 can be prolonged in neonates, patients elderly, patients with liver disease. T1 / 2 is not measurable
Application of the substance DiazepamAs a sedative, anxiolytic and hypnotic.
Neurology and Psychiatry.
All types of anxiety disorders, including neuroses, psychopathy, neurosis and psychopathic state, accompanied by anxiety, fear, increased irritability, emotional stress; disturbing syndrome of endogenous mental illness, including in schizophrenia (adjuvant in the complex therapy), with organic brain lesions, including cerebrovascular disorders (in combination therapy as an adjunct); senesto-hypochondriac, phobic and obsessive-compulsive disorder, paranoid-hallucinatory state; somatovegetative disorders, motor stimulation of different etiologies in neurology and psychiatry; tension headache; sleep disturbances; vertebral syndrome; withdrawal (alcohol, drugs), including: delirium tremens (in the complex therapy). In pediatric patients: neurotic and neurosis-like states, accompanied by emotional stress, anxiety, fear, increased irritability, headache, sleep disturbances, enuresis, mood disorders and behavior, etc. Cardiology.. Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, hypertension, and others. Anaesthesia and Surgery. Premedication before and immediately before surgery and endoscopic procedures, induction of anesthesia, as a component of combined anesthesia (if ataralgezia in combination with analgesics). Obstetrics and gynecology. Eclampsia, facilitating labor (for parenteral administration), premature labor, premature detachment of the placenta (for parenteral administration); menopausal and menstrual psychosomatic disorders. Dermatological practice. Eczema and other diseases accompanied by itching, irritability (complex therapy).
As an anticonvulsant.
Epilepsy (aid, as part of combination therapy), status epilepticus and severe recurrent seizures (for parenteral administration, the aid); tetanus.
As myo-relaxing agent.
Spasms of central origin associated with brain or spinal cord lesion (cerebral palsy, athetosis); spasm of skeletal muscles at the local trauma (aid); spastic conditions in other diseases of the musculoskeletal system - myositis, bursitis, arthritis, rheumatoid spondylitis, a progressive chronic polyarthritis; arthrosis, accompanied by a voltage of skeletal muscles.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, acute liver and kidney disease, severe liver failure, myasthenia gravis, suicidal tendencies, drug or alcohol dependence (except for the treatment of acute withdrawal syndrome), severe respiratory insufficiency, severe hypercapnia, cerebral and spinal ataxia, acute attack of glaucoma, angle-closure glaucoma, pregnancy (I term), breast-feeding, age up to 30 days.
Restrictions to application
Chronic respiratory distress, apnea during sleep, pronounced renal dysfunction, open-angle glaucoma (in the face of adequate therapy), up to 6 months (only for health in the hospital), pregnancy (II and III trimester).
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
It contraindicated in I trimester of pregnancy (increases the risk of congenital malformations). In II and III trimester of pregnancy is possible if the expected effect of therapy outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. At the time of treatment should stop breastfeeding.
Side effects of substance Diazepam
From the nervous system and sensory organs: fatigue, drowsiness, fatigue; ataxia, blunting of emotions, blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus, tremor, reaction speed and concentration, worsening short-term memory, dysarthria, slurred speech; confusion, depression, fainting, headache, dizziness; paradoxical reactions (severe agitation, anxiety, hallucinations, nightmares, fits of rage, inappropriate behavior); anterograde amnesia.
Cardio-vascular system and blood (blood, hemostasis): bradycardia, neutropenia.
From the digestive tract: violation of salivation (dry mouth or hypersalivation), nausea, constipation.
Other: allergic reactions (hives, rash), urinary incontinence, urinary retention, changes in libido, increased activity of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase, jaundice.
For parenteral administration: injection site reactions (thrombosis, phlebitis, infiltration formation); with the rapid on / in the introduction - hypotension, cardiovascular collapse, disturbance of respiratory function, hiccups.
Perhaps the development of addiction, drug dependence, withdrawal symptoms, after-effect syndrome (muscle weakness, decreased performance), rebound-a syndrome.
Interaction of substance Diazepam
Potentiate the effects of alcohol, anticonvulsants and antihypertensives, antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, analgesics (including opioids), sleeping medicines, general anesthetics, muscle relaxants, antihistamines drugs with a sedative effect. Analeptics, psychostimulants - reduce activity. Antacids can reduce the rate but not the extent of absorption of diazepam.
Isoniazid slows down diazepam (and increases its concentration in the blood). Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine, ketoconazole, fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, omeprazole) alter the pharmacokinetics and increase the duration of the effect of diazepam. Rifampicin concentration of diazepam decreases in blood. Erythromycin slows diazepam metabolism in the liver. Diazepam may alter plasma concentrations of phenytoin.
Overdose of substance Diazepam
Symptoms: oppression CNS varying degrees of symptoms (from somnolence to coma): expressed drowsiness, lethargy, weakness, loss of muscle tone, ataxia, prolonged confusion, oppression reflexes, coma; also possible hypotension, respiratory depression.
Treatment: induction vomiting and the appointment of activated charcoal (if the patient is conscious), gastric lavage through the probe (if the patient is unconscious), symptomatic therapy, monitoring vital functions, in / in a liquid (to increase urine output), if necessary ventilation. When driving the development should not be used barbiturates. As a specific antidote used BZ antagonist flumazenil receptors (in the hospital). Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Dosing and Administration of Diazepam Substances
Inside, in / in, in / m, rectally. The mode set is strictly individual, depending on the evidence, the disease, tolerance and others. Treatment should be started with the lowest effective dose corresponding to a particular form of pathology.
Usual dose for adults at intake: primary - 5-10 mg, daily - 5-20 mg, the maximum single - 20 mg, the maximum daily 60 mg.
The on / in and / m the introduction of an average single dose for adults - 10 mg, the average daily - 30 mg, the maximum single - 30 mg, the maximum daily 70 mg. The duration of treatment by parenteral administration should not be more than 3-5 days (after which, if necessary, moving to ingestion), the total duration of treatment should be as short as possible and should not exceed 2-3 months (including the period of gradual reduction of the dose) . Increasing the duration of treatment in excess of 2-3 months is possible only after repeated careful evaluation of the patient. Before re-rate break should be at least 3 weeks.
The dose and duration of treatment for children picked individually, depending on the nature of the disease, age and body weight of the child.
Patients elderly and patients with impaired liver function should begin treatment with lower doses.
Precautions for Diazepam substance
Not recommended for monotherapy of benzodiazepines with a combination of anxiety with depression (suicide attempts are possible). Due to the possibility of paradoxical reactions, including aggressive behavior, used with caution in patients with personality and behavioral disorders. Paradoxical reactions are more common in children and elderly patients. In the event of paradoxical reactions of diazepam should be discontinued.
During treatment with diazepam unacceptable consumption of alcoholic beverages.
should not be used during the drivers of vehicles and people whose work requires quick mental and physical reactions, and is also associated with high concentration of attention.
The use of diazepam in children under 14 years of age is allowed only in clearly justified cases, the duration of treatment should be minimal.
When receiving diazepam (even at therapeutic doses) may develop addiction, formation of physical and psychological dependence. Depending risk increases when large doses and with increasing duration of the reception, as well as in patients with alcohol dependence and drug history. Abolition of diazepam should be carried out gradually by reducing the dose to reduce the risk of withdrawal symptoms and rebound-a syndrome. In abrupt cancellation after long-term use or high doses there is a withdrawal syndrome (headache and muscle pain, agitation, anxiety, confusion, tremors, convulsions), in severe cases - depersonalization, hallucinations, seizures (sudden elimination in epilepsy). Transient syndrome in which symptoms that caused the appointment of diazepam, resumed in a more pronounced form (rebound-Syndrome), may also be accompanied by changes in mood, anxiety, and others.
Prolonged use should be periodically monitored picture peripheral blood and liver function.
Application at doses above 30 mg (especially / or m / v) for 15 hours prior to childbirth can cause neonatal apnea, hypotension, hypothermia, and rejection of the other breast.
There were cases of benzodiazepine addiction.
Special instructions
Keep in mind that anxiety or tension associated with everyday stress usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
Not be mixed in the same syringe with other drugs diazepam (possibly settling on the walls of the drug). The on / in the introduction should be administered in a large vein and slowly, controlling the breathing function. Avoid contact of the solution into the artery and extravasal space.
Trading names of drugs with working substance Diazepam
Trade Name
Apaurin
Valium Roche
Diazepabene
Diazepam
Diazepam Nycomed
Diazepam-ratiopharm
Diazepex
Range
Relanium
Relium
Seduxen
sibazon
Sibazon injection 0.5%
Sibazon tablets

 Cart
Cart