Cortexin - Instructions for use, contraindications, Dosage
22 Dec 2016
Cortexin is widely used by doctors in neurological diseases and pathological processes associated with a disorder of brain function. The breadth of the spectrum efficiency covers all age groups, from newborns to the first day of life. The biological nature of the product allows you to run a short course of the internal mechanisms that restore the normal functioning of the brain. The effectiveness persists for several months. Security of Cortexin is confirmed practice of the drug in millions of patients, both in Russia and abroad.
Neuroprotection
This term is often found in medical publications, the media, in advertising of medicinal products. Neuroprotection possibilities inherent in the nature of the brain, the genes on the level of regulatory neuropeptides. Neuroprotection essence is that the healing process contributes not only to the protection of the affected group of neurons, but also ensure its continued operation. For medicine important question - whether there are adequate pharmacologic effects that can run these natural mechanisms and support them at the appropriate level? In this context, search, creation and testing of new pharmaceuticals are and will be one of the most important areas of modern pharmacology.
It is obvious that the search for new neuroprotective agents is a complex process that requires the combined efforts of physicians, biologists, pharmacologists at all stages. In this regard, special attention should be given peptide drugs. Despite their diversity, they share a number of common characteristics: low dosage, absence of marked toxic effects, softness and length of exposure. In general, it can be argued that the system of the body peptides, formed by millions of years of evolution, provides multi-level regulation of all functions, including the processes that lead ultimately to the neuroprotective effect. In terms of information exactly peptides are a universal language understandable and natural for the living organisms both on the system level and at the cellular level.
One of the successful examples of development based on the above principles, is Cortexin - a drug whose effectiveness is proven in the study of all possible levels: clinical, biological, cellular, genetic and molecular.
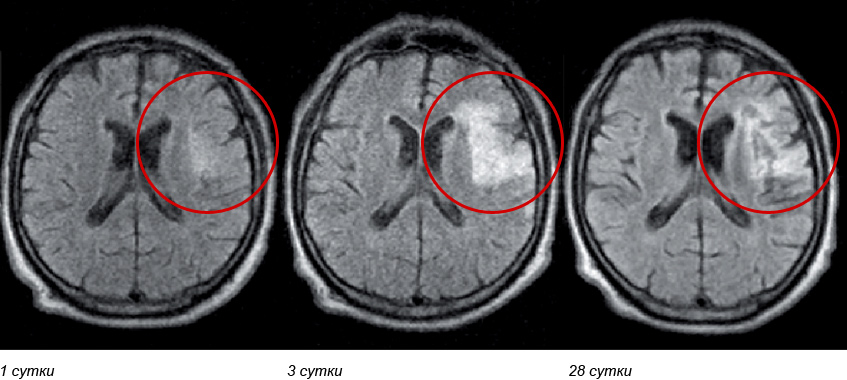
According to MRI in the right temporal region of the brain is determined by the lesion, the scope of which is clearly growing to 3 days. With this defeat on the 28 day is usually observed the formation of glial scar and post-stroke cysts. When using Cortexin, when a patient with an ischemic stroke is starting to get the drug in the first hours of the disease, along with a noticeable improvement in general health, and neurological clinical picture, the amount of brain damage to the hearth 28 days decreased by 40%. This observation illustrates the striking effect of the neuroprotective action of Cortexin.
According to MRI in the right temporal region of the brain is determined by the lesion, the scope of which is clearly growing to 3 days. With this defeat on the 28 day is usually observed the formation of glial scar and post-stroke cysts. When using Cortexin, when a patient with an ischemic stroke is starting to get the drug in the first hours of the disease, along with a noticeable improvement in general health, and neurological clinical picture, the amount of brain damage to the hearth 28 days decreased by 40%. This observation illustrates the striking effect of the neuroprotective action of Cortexin.
Terminology: Ischemia - Lack of blood supply to an organ or tissue site, caused by blockage or narrowing of the corresponding artery; ATP - ATP - nucleotide, plays a crucial role in the exchange of energy and substances in organisms; first compound is known as a universal energy source for all biochemical processes in living systems. The depolarization of the cell membrane - changing the electric potential on the cell membrane; Glutamate - an amino acid, the major excitatory neurotransmitter. Binding of glutamate neurons with specific receptors leads to neuronal excitation. NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors - receptors that provide carrying moments of the exciting neurons in the binding of glutamate; Caspases, NO-synthase - intracellular enzymes involved in the processes of cell death and oxidative stress.
The neuroprotective antiapoptotic action
Cortexin is a neuroprotectant which has a therapeutic effect, from the first hours after ischemic brain damage. This means that its main target is the penumbra area - site of the nervous tissue surrounding the lesion, is experiencing oxygen starvation and energy, but temporarily, up to 6 hours, stay alive. The outcome of this process depends on the ability to restore nerve function, life and death of the patient. Cortexin has an impact on all parts of the pathological chain of molecular events leading to neuronal death. It is shown that Cortexin reduces neuronal apoptosis (programmed cell death), caused by excessive accumulation of glutamate.
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system. When stroke occurs excess release of glutamate, resulting in the start stage processes underlying neuronal death. In nervous tissue culture medium in glutamate administration also leads to neuronal death. If administered simultaneously with glutamate substance having neuroprotective effect, the neuronal cell death is reduced. This figure shows the results of a study of neuroprotective properties Cortexin in vitro: while the introduction of glutamate Cortexin has a pronounced neuroprotective effect in the nanogram range of concentrations (* p <0,05 as compared to the control group).
Recovery of ATP synthesis
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP abbr.) - A nucleotide that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and substance in the body, the universal energy source for all cells in the body. The fall of ATP content in brain cells is a central element of all pathological processes taking place on the background of cerebral ischemia. Reduced synthesis and an increase in ATP consumption is shown immediately after the start of the nervous tissue ischemia Recent studies have demonstrated that Cortexin is able to restore ATP content in neurons.
The study demonstrated the ability to run processes Cortexin natural regeneration of ATP in the mitochondria of nerve cells. Since the fall of the ATP level is one of the main causes leading to the death of nerve cells in stroke patients, the restoration of this indicator under the influence of Cortexin explains its clinical effectiveness.
Neurotrophic action
Peptides of Cortexin have direct and indirect effects on neurotrophic cells. The main mechanisms of these effects are based on changes in gene regulating the synthesis own neurotrophic factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF).
Stimulation of neurite outgrowth in cultures of chicken embryo brain. In tissue culture, neurite growth in nerve (nerve cell process by which nerve impulses coming from the cell body to organs and other nerve cells) occur only in the presence of neurotrophic factors. In this test a sample to determine, Cortexin its neurotrophic effects: on the right micro-photograph the entire field around the nerve tissue islet employed branched neurite network, while, in the control (left micro-photograph) growth of neuronal processes virtually not observed ( the photos shows the results of testing a series of drug.
Thus, numerous independent studies convincingly demonstrate the existence of Cortexin multiple effects, affecting the regulation of apoptosis cascade, expression neurotrophic factors, the energy supply of the nerve cell and mitochondrial potential, functioning of glutamate receptors and regulation of the concentration of calcium ions into the cell, which in combination provide the neuroprotective and neurotrophic effect of the drug, and, as a result, high efficiency of the treatment and improving the quality of life of the patient.
Name of grouping: The polypeptides of the cerebral cortex of cattle.
Cortexin Dosage form: lyophilisates for solution for intramuscular injection.
Pharmacodynamics: KORTEKSIN® contains a complex of low-molecular weight water-soluble polypeptide fractions of penetrating the blood-brain barrier directly to the nerve cells. The drug has nootropic, neuroprotective, antioxidant and tissue-specific action.
The mechanism of Cortexin action caused by activation of neurons of the brain peptides and neurotrophic factors; optimizing the balance of excitatory and inhibitory metabolism of amino acids, dopamine, serotonin; GABAergic influence; decrease in the level of paroxysmal convulsive brain activity, the ability to improve its bioelectric activity; preventing the formation of free radicals (lipid peroxidation products).
Indications for use: In the treatment of cerebral circulatory disorders, traumatic brain injury and its consequences, encephalopathies of various origins, cognitive impairment (memory loss and thinking), acute and chronic encephalitis and encephalomyelitis, epilepsy, asthenic conditions (suprasegmental autonomic dysfunction), decreased learning ability, delayed psychomotor and speech development in children with various forms of cerebral palsy.

 Cart
Cart