Aminophenylbutyric acid - Active Substances. Instruction and Application, Dosage
26 Dec 2016
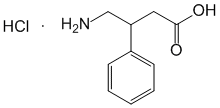
Name: Aminophenylbutyric acid
The Latin name of the substance Aminophenylbutyric acid
Acidum aminophenylbutyricum (genus. Acidi aminophenylbutyrici)
chemical name gamma-beta-Amino-phenylbutyric acid hydrochloride
Formula - C10H14ClNO2
Therapeutic agents of Aminophenylbutyric acid:
Nootropics
Anxiolytics
The nosological classification (ICD-10)
F10.3 abstinence
F40.9 Phobic anxiety disorder, unspecified
F41.2 Mixed anxiety and depressive disorder
F41.9 Anxiety disorder, unspecified
F42.0 Predominantly obsessional thoughts or reflections
F48 Other neurotic disorders
F48.9 Neurotic disorder, unspecified
F60.2 antisocial personality disorder
F95 Tiki
F98.0 Enuresis inorganic nature
F98.5 Stuttering [hesitation]
G47.0 Disorders of falling asleep and maintaining sleep [insomnia]
H81.0 Ménière's Disease
H81.9 Violation of vestibular function, unspecified
H83.0 Labyrinthitis
R42 Dizziness and disturbance stability
R45.1 Restlessness and agitation
R53 Malaise and fatigue
Motion sickness when moving T75.3
Z100.0 * Anesthesiology and premedication
CAS code - 1078-21-3
Characteristics substance Aminophenylbutyric acid
The white crystalline powder. It is very easily soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, pH water (2.5%) solution was 2.3-2.7.
The chemical structure can be seen as a phenyl derivative of GABA, as well as a phenylethylamine derivative.
Pharmacology
Mode of action - nootropic, anxiolytic.
Influences on GABA receptors in the central nervous system, facilitate GABAergic neurotransmission, improves the bioenergetic processes in the brain. It eliminates tension, restlessness, anxiety, fear, and improves sleep; It extends and enhances the action of hypnotics and antipsychotics, narcotic analgesics. Reduces the symptoms of fatigue and vasovegetative symptoms (including headache, a feeling of heaviness in the head, insomnia, irritability, emotional lability), enhances mental performance; improves attention, memory, speed and accuracy of sensorimotor reactions. When fatigue improves mood, increases interest and motivation activities. Extends latency and reduces the duration and severity of nystagmus.
Absorption from the gastrointestinal tract - a tall, well into all tissues, and the BBB (in brain tissue found around 0.1% of the administered dose, people young and old - much more). It is metabolized primarily in the liver (80-95%) to pharmacologically inactive metabolites. Approximately 5% is excreted in the urine in unchanged form. Not accumulates.
Application of the Aminophenylbutyric acid substance
Asthenic syndrome, anxiety and neurotic states (worry, anxiety, fear), obsessive-compulsive disorder, insomnia and night anxiety in the elderly, psychopathy, premedication before surgery, otogenny labyrinthitis, vestibular disorders infectious, traumatic and vascular genesis, including Meniere's disease, vertigo, alcohol withdrawal syndrome (in the complex therapy), the prevention of motion sickness when kinetoses; children - stuttering, tics, enuresis.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity.
Restrictions to application
Erosive-ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, liver failure, pregnancy, breast-feeding.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
The caution (not enough clinical experience). In experimental studies found no mutagenic, teratogenic and embryotoxic action.
Category effects on the fetus by FDA - is not defined.
Side effects of Aminophenylbutyric acid substance
Drowsiness, nausea, headache (with the first receptions); strengthening of irritability, agitation, anxiety, dizziness, allergic reactions.
Interaction of Aminophenylbutyric acidsubstance
Enhance and prolong the effect of hypnotics, antiparkinsonian and antiepileptic drugs, antipsychotic drugs, narcotic analgesics.
Overdose of Aminophenylbutyric acidsubstance
Symptoms: severe drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, hepatic steatosis (receiving more than 7 g), eosinophilia, decreased blood pressure, renal function.
Treatment: gastric lavage, the appointment of activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy.
Dosing and Administration of Aminophenylbutyric acid Substances
Inside. Adults and children over 14 years - by 0.25-0.5 g 3 times a day, if necessary - up to 2.5 g / day, the course of 2-3 weeks. Patients over 60 years - no more than 0.5 g per reception. Children up to 8 years - 0.05-0.01 g, 8-14 years - 0.25 g three times a day. The maximum single dose: adults - 0.75 g, patients older than 60 years - 0.5 g, for children up to 8 years - 0.15 g, 8-14 years - 0.25 g Relief of alcohol withdrawal syndrome: in the first days of treatment 0,25-0,5 g 3 times a day and night to 0.75, with a gradual decrease to a standard dose for adults. Otogennyh labyrinthitis and Meniere's disease in acute: 0.75 g 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days, then at reducing the severity of vestibular disorders at 0.25-0.5 g 3 times a day for 5 7 days, followed by 0.25 g per day for 5 days. In less severe conditions - 0.25 g 2 times a day for 5-7 days and then 1 time a day for 7-10 days. Dizziness dysfunction of the vestibular analyzer vascular and traumatic genesis: 0.25 g 3 times a day for 12 days. Prevention of motion sickness: 0.25-0.5 g once for 1 hour before the intended trip.
Precautions for Aminophenylbutyric acid substance
With prolonged use is necessary to monitor liver function and peripheral blood.
Be wary of during the drivers of vehicles and people skills relate to the high concentration of attention.
Special instructions
Ineffective after the pronounced effects of motion sickness (vomiting, dizziness, etc.).
Trading names of drugs with working Aminophenylbutyric acid substance
Trade Name
Aminophenylbutyric acid
Anvifen
Noofen, Noophen
Phenibut
Phenibut tablets

 Cart
Cart