Oxazepam - Active Substances. Instruction and Application, Dosage
26 Dec 2016
Name: Oxazepam
The Latin name of the substance Oxazepam
Oxazepamum (genus Oxazepami)
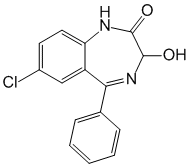
Chemical name: 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
Formula - C15H11ClN2O2
Therapeutic substances Oxazepam - anxiolytics
The nosological classification (ICD-10)
F10.3 abstinence
F32 Depressive episode
F34.1 Dysthymia
F40.2 Specific (isolated) phobias
F41.1 Generalized anxiety disorder
F41.2 Mixed anxiety and depressive disorder
F43.0 Acute stress reaction
F43.1 Post-traumatic stress disorder
F43.2 Disorder adaptive reactions
F45 Somatoform disorders
G47.0 Disorders of falling asleep and maintaining sleep [insomnia]
N94.3 syndrome premenstrual tension
N95.1 menopausal and menopausal status of women
R45.0 Nervousness
R45.4 Irritability and anger
CAS code - 604-75-1
Characteristics substance Oxazepam
Anxiolytic of benzodiazepine group.
White or white with a slightly yellowish white crystalline powder and odorless. Practically insoluble in water, soluble enough in ethanol, chloroform, ether, is soluble in dimethylformamide.
Pharmacology
Mode of action - anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic.
It interacts with specific benzodiazepine receptors located in the postsynaptic GABAA receptor complex in the brain's limbic system, the ascending activating reticular formation of the brain stem and neurons of lateral horns of the spinal cord. It increases the sensitivity of GABA receptors to neurotransmitter (GABA). This increases the frequency of the opening in the cytoplasmic membrane of neurons transmembrane channels for incoming currents chlorine ions. There membrane hyperpolarization and inhibition of neuronal activity. Thus enhanced inhibitory effect of GABA in the CNS.
It has a calming, sedative and anxiolytic effect on the CNS. It relieves emotional stress, reduces anxiety, fear, anxiety, promotes the onset of sleep. It relieves the symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal. It has little muscle relaxant (central) and the anticonvulsant effect.
For oxazepam characterized by a large breadth of therapeutic action (a big difference between an effective dose and a dose causing side effects).
The tolerance and toxicity studies of oxazepam in different animal species (mice, rats, dogs) showed a significant difference in the effective doses (anxiolytic effect) and dose causing side effects. Thus, mice at oral doses were effective oxazepam almost 10 times lower than the doses that cause ataxia (rotabar-test) and sedation (cancellation of spontaneous motor activity).
In the two-year studies in rats when administered doses 30 times higher than MRDCH, found an increase in the incidence of benign tumors follikulyarnokletochnyh thyroid adenomas of the testes (interstitsialnokletochnyh) and adenomas of the prostate gland. In a nine-month study in rats at doses 35-100 times higher than a daily dosage for humans, a dose-dependent increase in observed incidence of hepatic adenomas. At the same time, there is no evidence that the clinical use of oxazepam is associated with the occurrence of tumors.
After oral administration is slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax is achieved in 1-4 hours Linking blood protein -. 97%. The equilibrium concentration in the blood is achieved within several days after the beginning of reception. Distributed in the body. It passes through GEB, placental barrier, enters the breast milk. Treated glucuronidation in the liver, there is no active metabolites. T1 / 2 is an average of 8.2 hours (5.7 - 10.9 h). Write mainly kidneys as glucuronide. When you receive repeated doses accumulate a minimum.
Application of the substance Oxazepam
Neuroses, psychopathy, neurosis and psychopathic state, accompanied by fear, anxiety, increased irritability, sleep disorders, etc .; senesto-hypochondriacal disorders and obsession (especially for poor tolerance of other anxiolytics); autonomic disorders in women associated with menopause, premenstrual syndrome; reactive depression (as part of combination therapy with antidepressants), alcohol withdrawal syndrome (in combination therapy).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, psychosis, severe myasthenia gravis, acute renal and / or hepatic insufficiency, pregnancy (especially I trimester), breast-feeding, age up to 6 years.
Restrictions of application of Oxazepam
The tendency to abuse of psychotropic drugs.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Contraindicated during pregnancy (especially in I trimester). At the time of treatment should stop breastfeeding.
Side effects of Oxazepam substance
From the nervous system and sensory organs: drowsiness (usually within the first days of treatment), fatigue, dizziness, fatigue, headache, memory impairment, muscle weakness, ataxia, tremor, slurred speech, paradoxical reaction in psychiatric patients, including . psychomotor agitation, anxiety.
Other: dry mouth, nausea, dyspepsia, leukopenia, abnormal liver function (including jaundice), allergic reactions, fainting, changes in libido.
Possible addiction, drug dependence, withdrawal syndrome.
Interaction
It enhances the effect of oppressive central nervous system, including hypnotics, antiepileptic drugs, antipsychotics, funds for general anesthesia, alcohol.
Overdose of Oxazepam
Symptoms: oppression CNS varying degrees of symptoms (from somnolence to coma) - drowsiness, confusion, lethargy; in more severe cases (especially in patients receiving other drugs which depress the central nervous system, or alcohol) - ataxia, decreased blood pressure, hypnotic state, coma.
Treatment: induction of vomiting, gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy, monitoring vital functions. In severe hypotension - introduction of norepinephrine. The specific antidote - benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil receptors (introduction only in a hospital). Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Dosing and Administration of Oxazepam
Inside (regardless of the meal). The dose and duration of treatment are chosen strictly individually, depending on indications and therapeutic effect. The initial single dose for adults - 5-10 mg, in-patient treatment, the mean daily dose of 30-50 mg, the maximum dose in the hospital - 120 mg / day. The average duration of the course is 2-4 weeks.
The dose has not been established for children 6-12 years.
Precautions substance Oxazepam
With caution used in the predisposition to arterial hypotension, particularly in elderly patients (due to the possibility of cardiac activity), increased risk of development of drug dependence.
It should not be used with MAO inhibitors, phenothiazine derivatives. The likelihood of overdose symptoms increases with simultaneous reception of oppressive central nervous system, or alcohol. During treatment excludes alcohol intake.
Do not use for a long time (due to the risk of drug dependence). If necessary, long-term treatment (months) course should be done by the method of intermittent therapy, stopping the reception for a few days followed by the same dose of individually selected. The lifting should be done gradually. With a sharp lifting of Oxazepam may experience withdrawal symptoms (tremor, convulsions, abdominal or muscle cramps, vomiting, sweating), most commonly appearing after administration of high doses or long-term treatment.
In long-term treatment is necessary to monitor liver function and pattern of peripheral blood.
Do not apply to drivers of vehicles and people skills relate to the high concentration of attention.
Special instructions for Oxazepam
It is recommended in the treatment of anxiety, tension, agitation, irritability, debilitated patients, elderly people and patients with residual symptoms of traumatic or infectious lesions of the central nervous system.
Keep in mind that anxiety or tension associated with everyday stress usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
Trading names of drugs with Oxazepam working substance
Trade Name Index
Nozepam, Nozepam tablets 0.01 g, Oxazepam, Tazepam

 Cart
Cart