Hydroxyzine - Active Substances. Instruction and Application, Dosage
28 Dec 2016
Name: Hydroxyzine
The Latin name of the substance Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzinum (genus Hydroxyzini)
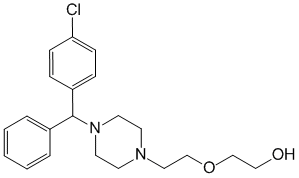
Chemical name: 2- [2- [4 - [(4-chlorophenyl) phenylmethyl] -1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] ethanol (as the dihydrochloride or embonate)
Formula - C21H27ClN2O2
Therapeutic substances Hydroxyzine - anxiolytics
The nosological classification (ICD-10)
F10.2 alcohol dependence syndrome
F10.3 abstinence
F11 Mental and behavioral disorders due to use of opioids
F41.1 Generalized anxiety disorder
F43.0 Acute stress reaction
L29 Itching
R45.1 Restlessness and agitation
R45.4 Irritability and anger
R45.7 State of emotional shock and stress, unspecified
Z100 * CLASS XXII Surgical practice
CAS code - 68-88-2
Characteristics substance Hydroxyzine
Diphenylmethane derivative. Hydroxyzine hydrochloride - white powder, odorless, very soluble in water, the molecular weight of 447.83.
PharmacologyMode of action - a sedative, anxiolytic.
It inhibits the activity of certain subcortical structures of the central nervous system, blocking the central m-choline and of H1-histamine receptors.
Characterized by pronounced sedative effects and moderate anxiolytic activity. It has a positive influence on cognitive abilities, improves memory and attention. It does not cause mental dependence and addiction, chronic administration were observed withdrawal. It has also an anticholinergic, antispasmodic, anti-histamine effect. It relaxes smooth muscles, has a bronchodilator and analgesic effect, has antiemetic, and muscle relaxant action and a moderate inhibitory effect on gastric secretion. Reduces itching hives, eczema, dermatitis and others.
Sedation is usually observed after 10-45 min after oral administration (depending on formulation), antihistamine - 1 hour after ingestion. Patients with liver disease anti-histamine effect can last up to 96 hours.
Mutagenic and carcinogenic effects have been identified.
Introduction hydroxyzine pregnant female rodents (mice, rats, rabbits) at doses much higher than the therapeutic dose for humans, led to the emergence of fetal malformations in the fetus.
If ingestion is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, the Cmax is achieved in 2 hours. Passes through GEB and placenta (in fetal tissues is concentrated to a greater extent than the parent). It is metabolized in the liver, the major metabolite - cetirizine. T1 / 2 depends on the age of the patient and is 7 hours (in children 2-10 years), 20 hours (adults), 29 hours (in the elderly and elderly); in patients with liver disease increased to 37 h. Write mainly kidneys (0.8% unchanged).
Application of the substance Hydroxyzine
Relief of anxiety, agitation, inner tension, irritability, neurological, mental (generalized anxiety and adjustment disorders) and somatic diseases; alcohol withdrawal syndrome; premedication and postoperative period (in combination therapy); itching (symptomatic therapy).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, including to cetirizine, aminophylline or ethylenediamine; porphyria, pregnancy, labor and delivery, breast-feeding.
Restrictions of application of Hydroxyzine
Glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy with clinical symptoms (including difficulty urinating, constipation), myasthenia gravis, dementia, susceptibility to seizures, kidney and / or liver failure.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Contraindicated during pregnancy.
Category effects on the fetus by FDA - is not defined.
At the time of treatment should stop breastfeeding (unknown if excreted into breast milk).
Side effects of Hydroxyzine substance
From the nervous system and sensory organs: drowsiness, weakness (in the early days of admission), headache, dizziness.
Other: increased sweating, tachycardia, nausea, allergic reactions, dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation, eye accommodation.
Interaction
It is dampening effect on the central nervous system narcotic analgesics, barbiturates, tranquilizers, hypnotics (individual selection of doses required), alcohol. Prevents the development of the pressor effect of epinephrine, anticonvulsant activity of phenytoin, the action of betahistine and cholinesterase blockers. Reduces side effects (from the stomach), theophylline and beta2-agonists.
Interactions with drugs that cause changes in the ECG
Hydroxyzine in high doses may cause disturbances ECG, including lengthening the interval QT, so concomitant use with other drugs capable of causing cardiac abnormalities may increase the likelihood of arrhythmias and sudden death.
Clinical evidence, mechanism, importance and caution
In 25 elderly patients with psychosis treated with hydroxyzine 300 mg, ECG changes after 9 weeks were moderate, with the exception of T-wave changes (detected in 9 people and is usually observed in the position 1,2 AVL and V1-6). In each case, T wave height was reduced, expanded, flattened; QT interval is usually extended. At repeated research in a few patients, one of whom received 400 mg of hydroxyzine, similar results were obtained, with more pronounced changes, which consisted of a marked weakening of the myocardial repolarization. Please pay attention to Noopept.
On the basis of these observations, it is assumed that other drugs that cause changes in the ECG (antiparkinsonian drugs, atropine, lithium carbonate, phenothiazines, quinidine, procainamide, thioridazine, tricyclic antidepressants) may intensify and exacerbate the changes caused by Hydroxyzine, and increase the risk of sudden death. Further study is needed to evaluate the practical significance of these possible interactions. However, you should avoid joint use of two or more drugs prolonging the QT interval, due to the risk of additive effects, which may lead to severe and potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, such as a pirouette.
Overdose of Hydroxyzine
Symptoms: hyper-sedation, tremor, convulsions, hallucinations, confusion, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting.
Treatment: induction vomiting (in the absence of spontaneous), gastric lavage, general supportive measures, including monitoring of vital body functions. If hypotension - introduction of norepinephrine (but not epinephrine). There is no specific antidote. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Dosing and Administration of Hydroxyzine
Inside, in / m. Adults: in general practice - 25-100 mg / day in divided doses, in psychiatry - up to 300 mg / day. The usual duration of the course of treatment - 4 weeks. In anesthesiology: / m, adults - 100-200 mg / day, for sedation - 50-200 mg.
Children appoint depending on the age and body weight.
In simultaneous treatment means, oppressive central nervous system, or holinoblokatorami, need a dose adjustment. The dose should be reduced in elderly patients (treatment start with half the therapeutic dose), renal and liver failure.
Precautions substance Hydroxyzine
If side effects such as sleepiness and weakness do not disappear after a few days of treatment, the dose should be reduced. Avoid joint appointment with MAO inhibitors. To use caution in patients prone to arrhythmia or receiving antiarrhythmic drugs, and in patients prone to convulsive reactions.
During treatment should avoid drinking alcohol. When the need for allergy tests receiving hydroxyzine should be discontinued 5 days prior to the study. Be wary of during the drivers of vehicles and people skills relate to the high concentration of attention.
Special instructions for Hydroxyzine
Injectable forms of hydroxyzine are only for i / m injection and should not be administered in / in / and or s / c. When i / m administration should make sure that the needle does not hit in any vessel. When administered to the skin the drug may cause tissue damage.
Trading names of drugs with Hydroxyzine working substance
Trade Name Index
Atarax, Hydroxyzine, Hydroxyzine Canon, Hydroxyzine hydrochloride

 Cart
Cart