How to treat fungal diseases
21 Sep 2018
Currently, fungal - mycotic - infections affect about 20% of the world's population. More than 100 thousand mushrooms are known, of which about 50 thousand are pathogenic for humans. In this case mycosis is very contagious.
The most common mycoses with a lesion of smooth skin and nail plates - onychomycosis. The causative agent of onychomycosis can be dermatophytes (Trichophyton rubrum) that affect the nail plates on the toes of the feet, brushes, smooth skin, as well as long and hairy hair, and Trichophyton interdigitale - the nails that damage the toes and the interdigital folds, the upper third of the sole and the arch of the foot. Often, onychomycosis causes yeast-like fungi of the species Candida and mold fungi - Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Aspergillus, Fusarium and others.
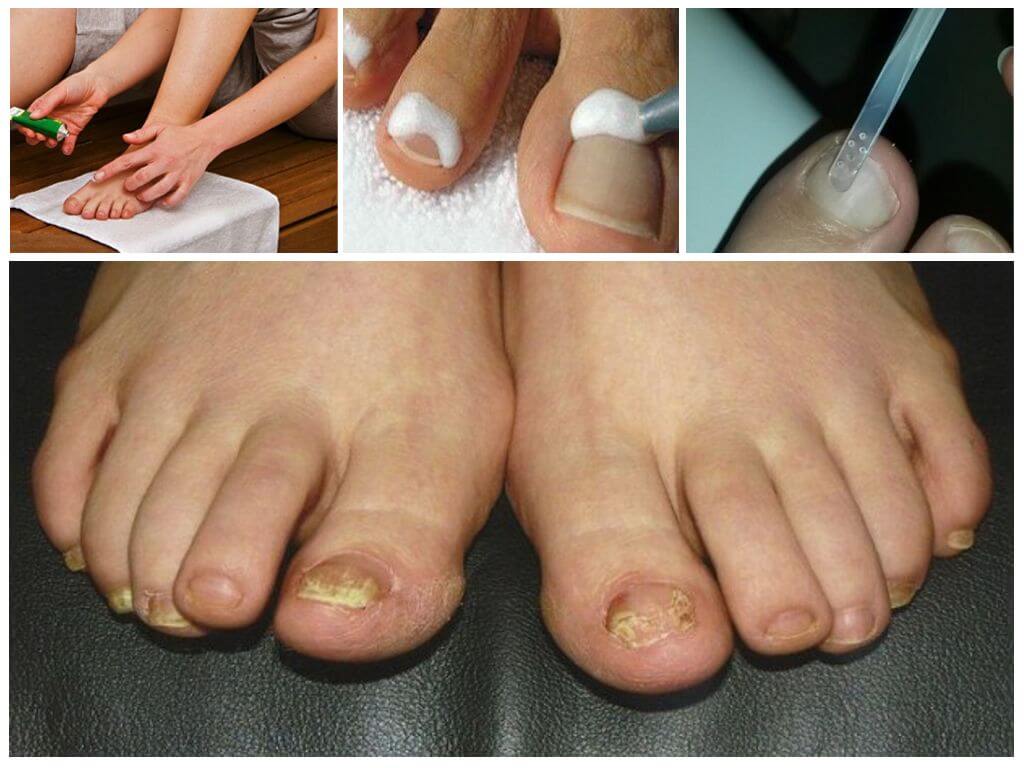
The defeat of the nail plates can proceed according to the normotrophic type - only the color of the nails changes: in their lateral areas, spots and bands appear, the color of which varies from white to yellow, gradually the whole nail changes its color while retaining its thickness.
In hypertrophic type, subungual hyperkeratosis is attached to the changed color; the nail loses color, becomes dim, thickens and deforms.
For the onycholitic type, a dull brownish-gray color of the affected part of the nail, its atrophy and rejection from the bed is characteristic, the exposed area is covered with loose hyperkeratotic scales. In 15-25% of patients with mycosis, the stop fungal process spreads primarily to large skin folds, then to other parts of the skin. The effects of mycosis feet are quite serious. Under the influence of fungi and the products of their vital activity, polyvalent sensitization is formed, which leads to an increase in the frequency of allergic skin diseases, mucous membranes, attachment of eczematous complications, drug intolerance, especially antibiotics of the penicillin series. In addition, through erosion and cracks in the macerated, loosened horny layer of the skin, bacteria easily penetrate. Bacterial complications are characterized by resistance to therapy, bacteria under the influence of antibiotic substances produced by fungi, acquire increased resistance to antibiotics.
Combating the fungus from the outside and inside
Etiotropic treatment of onychomycosis happens:
- local (external) - the antifungal drug is applied to the smooth skin or the affected nail;
- systemic - the drug is prescribed inside, and it enters the nail plate through the blood.
To the requirements for antifungal drugs, in addition to their effectiveness, include a wide range of antifungal activity, rapid absorption, safety (the absence of common and local side effects), as well as ease of use.
Means of local therapy. If the patient has various diseases (chronic hepatitis, nephritis, pathology of the cardiovascular system), as well as with superficial mycosis and mycosis of smooth skin, the main principle of treatment is the appointment of local antifungal therapy (ointments, creams, gels, sprays, solutions and varnishes ). Antifungal components of these forms do not penetrate through the nail plate, so the drugs are applied to the smooth skin or to the naked nail bed - they are rubbed 2-3 times a day until a healthy nail plate grows.
Drugs containing only antimycotic are isolated, for example: bifonazole (1% cream, 1% solution, spray, powder), isoconazole (1% cream), ketoconazole (2% cream), clotrimazole (1% ointment, 1% solution, 1% cream, 2% cream, suppositories), miconazole (2% cream), econazole (1% cream, 10% solution), naphthiphine (1% cream, 1% solution), terbinafine (1% cream), natamycin (2% cream), chloronitrophenol (1% solution).
Drugs of double action, which, in addition to antimycotics, include anti-inflammatory substances: clotrimazole and betamethasone (cream), miconazole and mazipredon (ointment), isoconazole and diflucortolone (cream).
Preparations of triple action - with antifungal, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory action: clotrimazole, gentamicin and betamethasone (cream, ointment), natamycin, neomycin and hydrocortisone (cream, ointment, lotion).
Very convenient for use in local therapy of onychomycosis varnishes (with active substance 8% cyclopyrox and 5% amorolfin). They differ not only in high fungicidal activity against dermatophytes, molds and yeast-like fungi, but also antibacterial against gram-positive and gram-negative flora. To cure onychomycosis, 6 months of therapy is sufficient on the hands, 9-12 months on the feet.
A solution containing the active ingredient terbinafine hydrochloride (1%) is applied once a day. When applied, a thin film forms on the surface of the epidermis, from which the active component is released into the deeper layers in the therapeutic concentration for 13 days. Sprays, which include terbinafine and bifonazole, have a primary fungicidal effect.
At local use of preparations there are no systemic side effects, but when applied to the surface of the nail they do not always reach the pathogen capable of damaging not only the nail plate, but also penetrating into the nail bed, deep layers of the skin and even into the medullary canal of the fingers, especially with total defeat a nail plate. As practice shows, local treatment alone, in most cases, does not lead to complete recovery of patients.
Preparations of systemic action. Systemic therapy provides penetration of drugs into the nails through the blood. Although it does not allow you to immediately create in the nail such high concentrations as with topical application, but the supply of the drug in the nail bed and matrix with systemic therapy is guaranteed. Many systemic drugs accumulate in the nail matrix in quantities far exceeding the minimum inhibitory concentrations, and are able to remain there after the treatment is over.
There are 3 groups of compounds created for the systemic treatment of fungal infections in humans:
- inhibitors of ergosterol biosynthesis; it is the main sterol of the fungal cell and is necessary for the propagation of fungi;
- allylamines, squalene epoxidase inhibitors, blocking the conversion of squalene to squalene epoxide);
- azoles, inhibiting the activity of fungal cytochromes P-450;
- morpholines inhibiting delta14-reductase and delta8-delta7-isomerase.
Synthetic antimycotics of the azole series include itraconazole and fluconazole. Itraconazole has the widest spectrum of action on dermatophytes, different species of Candida and many mold fungi found in onychomycosis. At the distal ends of the nail plate, itraconazole can be detected after 1 week of treatment. In the matrix, the drug accumulates and is excreted only when the new nail plate grows, therefore, the effective concentration of the drug after its abolition is maintained in the nails on the hands for another 3 months, and on the legs - for 6-9 months with a 3-month course of treatment.
Fluconazole in the treatment of onychomycosis is used according to the pulse therapy scheme, the duration of which depends on the form and localization of onychomycosis: about 6 months with nail damage on the hands, up to 12 months on the legs.
Terbinafine (an allylamine derivative) is highly effective and safe in the treatment of onychomycosis, the drug can be used in children. But many yeast fungi, in particular Candida albicans, are resistant to terbinafine. At infections of fingernails or nails on arms or hand the term terbinafine treatment makes 6 weeks, at infections of fingernails or nails on legs or foots - 12 weeks (3 months).
The above drugs are metabolized in the liver with cytochrome P-450, but itraconazole, in addition, interacts with this enzyme, disrupting the metabolism of many medications, which it somehow influences. Hepatic complications from increasing the level of hepatic enzymes to the possibility of hepatitis are higher in itraconazole than in terbinafine (0.3-5% vs. 0.1%, respectively).
Ketoconazole, a synthetic preparation from the class of azoles, has a wide spectrum of action, but many mold fungi - causative agents of non-dermatophytic onychomycosis - are resistant to ketoconazole. With onychomycosis, the treatment takes 4-6 months and 8-12 months - with onychomycosis stops. The main toxic effect of ketoconazole is its effect on the liver. An increase in the concentration of hepatic transaminases during treatment is observed in 5-10% of patients taking ketoconazole.
The greatest efficacy of mycosis therapy is still achieved with combined etiotropic treatment, which combines the administration of a systemic antimycotic and a local drug.
It is also necessary to remember the prevention of the disease, which includes personal hygiene, nail and foot skin care, the prophylactic use of antifungals after exercise, visits to public institutions (saunas, swimming pools), disinfection of shoes and bath, sex and pedicure accessories, once a week For prevention, you can cover your toenails with antifungal lacquer.
Many people with foot mycosis try to start treatment on their own, which in most cases does not bring the desired effect, but only aggravates the course of the disease (spreading skin rashes, involving more nail plates and complications in the form of eczematiza- tion), so treatment should be done after consultation of a specialist - a doctor-mycologist who correctly diagnoses and selects treatment for each individual patient individually.

 Cart
Cart