Frost - white nose
26 Jul 2018
It's so difficult to stay at home on New Year's Eve! Someone goes to the square to the city tree, someone goes to ride on the hill, someone just walks around the guests ... And yet not everyone sees in time how the fingers, ears, edges of the cheekbones, the tip of the nose, whiten and lose sensitivity . Meanwhile, this is the first sign of the beginning of frostbite - and at this stage, competent first aid is needed.
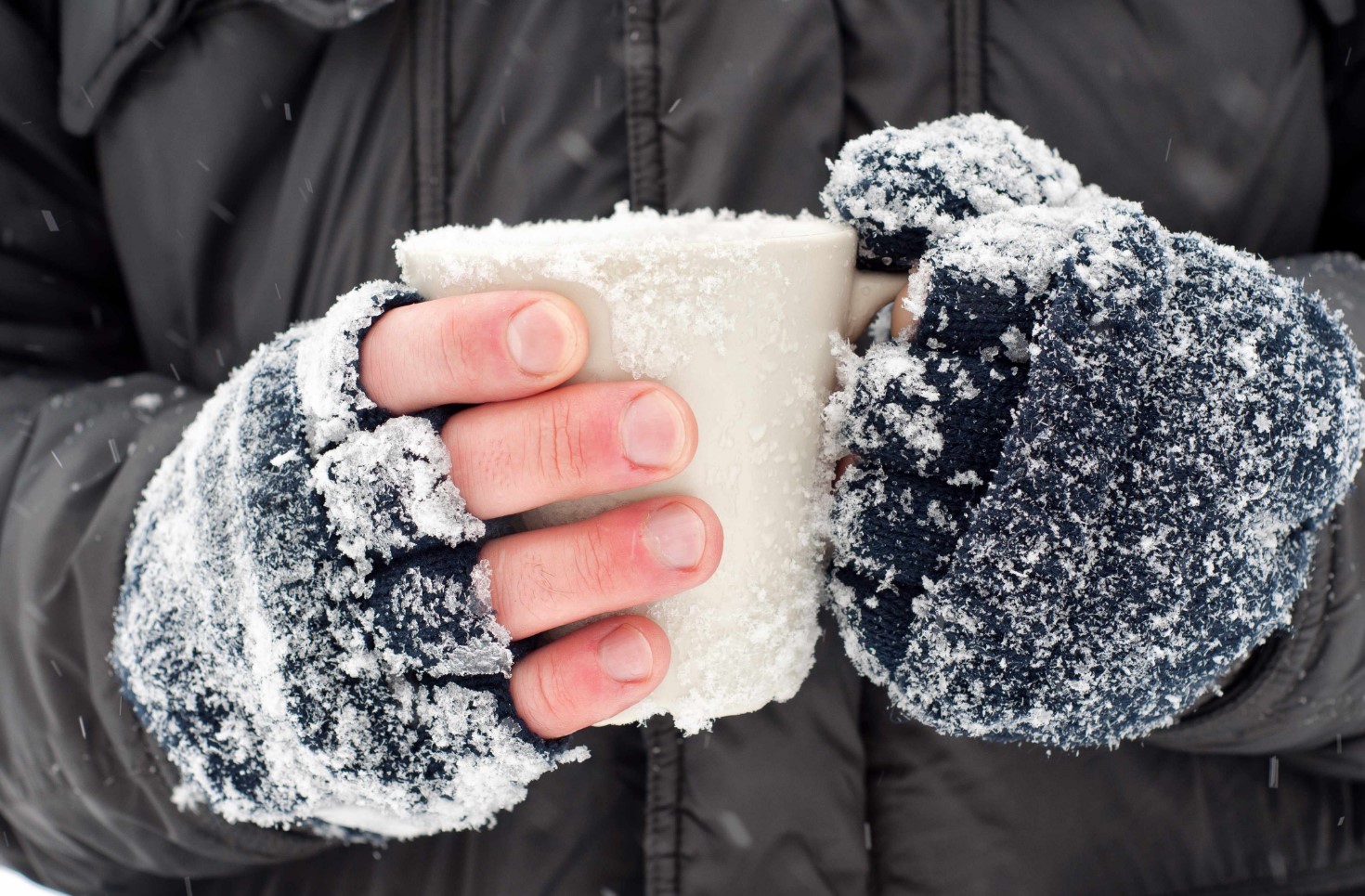

What can I freeze?
Frostbite (or frostbite - this term is considered by many to be more correct, but it is too ambiguous in the current colloquial speech ...) - this is a skin lesion under the influence of low temperatures. In some ways, it is similar to a burn and also refers to thermal injuries - but if the direct effect of high temperature on living tissues is of primary importance in burns, the mechanism of frostbite development is different. As you know, a person is warm-blooded, so even in cold weather our skin is "warmed" from the inside by the heat of our body, the frost and wind in this case damage (air) only the epidermis - the uppermost layer in contact with cold air. In deeper layers, the network of blood vessels plays the role of a heating system - the blood constantly enters the skin, gives it some of its heat and leaves to "warm up" in other parts of the body. If a person is dressed for the weather and comfortable, his face and hands are noticeably cool.
However, frostbite can also be something that is closed by clothing and especially shoes - even in winter boots or boots, the toes and feet as a whole may suffer, everyone knows well what "icy" and whitened they can be. Do not save and warm, thick socks, which can be worn even polar boots. Moreover - sometimes the thickness of socks is superfluous and harmful. The shoes become tight, the fingers lose mobility, the foot is tightly compressed - and the circulation of blood in the capillaries begins. The heating system "turns off", the legs gradually cool, the vessels from the cold narrow even more, insufficient blood supply and disruption of innervation lead to oxygen starvation of tissues, and this threatens them with necrosis...
Do not rub the frosted area with snow, coarse woolen cloth, etc. - at the same time, microtraumas, cracks and scratches are formed through which an infection can enter the weakened skin.
The same happens in open areas of the skin under the influence of frost, especially with the wind: the blood vessels contract from the cold, the circulation is disturbed - this is evident by the way the skin turns pale and white. This is the first stage of frostbite - the easiest, without deep lesions of the skin and especially lying below the tissues.
It should be noted that it is possible to frostbite even at an air temperature above zero - up to + 8 ° Ñ. Closely and wet clothes and shoes (lost their heat-protective properties), prolonged immobility, general weakening of the body, alcoholic intoxication (with its expansion after blood vessels contraction), strong wind, high humidity - the more such predisposing factors, the more "warm "There may be conditions in which a person can frostbite hands, feet and face.
Down in degrees ...
At the first degree of frostbite, impaired blood circulation leads to a feeling of numbness and tingling, whitening of the skin, with warming alternating red and crimson color and swelling, burning, sometimes very painful. If the frostbite place was heated quickly and correctly, the damaged tissues are restored within a week, after peeling of the frozen epidermis and the growth of a new layer. However, tenderness in the cold can last much longer.
More severe frostbite is similar in appearance to a burn: on the 2nd degree the affected skin is covered with bubbles with transparent contents, itch and it hurts, the healing may take up to 2 weeks. Prolonged exposure to cold leads to the third degree of frostbite - deep necrosis, the blisters become bloody, the skin darkens and flakes in the affected areas, scars form during healing (which takes more than a month). The heaviest, IV degree is the dying not only of the skin, but also of the underlying tissues, the skin completely loses sensitivity, the affected area swells from the swelling and turns black.
Particular danger is the transfer of decay products from dying tissues throughout the body - this leads to general intoxication and worsening of the condition of the victim. In such cases, sometimes you have to resort to surgery and excise the affected areas, and sometimes amputated frostbitten fingers, feet or brushes.
How to help?
The very first help that can be given to a person who has been frostbitten is to tell him what is happening: because of loss of skin sensitivity a person may not notice signs of frostbite. So if someone from the people who have met in the cold on the street or who went behind the shopping in the pharmacy turned white ears, the tip of the nose, the corners of the cheekbones, pay attention and advise what to do!
With frostbite of the I degree it is quite possible to cope independently, and it will pass with minimal consequences. It is necessary to warm the affected area, and even better - and the injured. Take him to a warm room, pour hot tea. Frozen skin should be warmed with warm hands - while only light massage is allowed, but not vigorous rubbing! With a cold lesion, the walls of the vessels become brittle, easily damaged. Do not rub the frosted area with snow, coarse woolen cloth, etc. - at the same time, microtraumas, cracks and scratches are formed through which an infection can enter the weakened skin. But a sterile cotton-gauze dressing or a warming compress will be quite appropriate, as well as a tablet of NSAIDs, which reduces pain, swelling, etc.
Heating baths with frostbite and hypothermia should not be hot - they will increase the severity of the lesion. If it is necessary to warm the victim in water, the temperature should be increased gradually from room temperature (24 ° C) to body temperature or slightly higher (37-38 ° C).
It is not recommended to warm up the injured limbs in the heater, the heating battery, especially at the open fire: the sensitivity of the frost-bitten tissues is reduced, and a person may not notice how he will get another thermal trauma - a burn.
Rubbing alcohol solutions, fat-based ointments, oils is sometimes permissible at I degree of frostbite, but the problem is that it is not immediately and not always possible to determine more severe degrees when such drugs are contraindicated. It is best to postpone the local preparations before the onset of skin peeling. She will come a few days after the injury. And then you may need moisturizing and nourishing creams, or even better - water based gels. There are ointments and balms, specially designed for the treatment of frostbite, but they are not always recommended to apply immediately - you must first carefully read the instructions! And, of course, it is unacceptable to use special "winter" cosmetics, not intended for treatment, but for the prevention of frostbite - it should be applied to healthy, not damaged skin.
If the frostbitten person warms up not at home, but at work, at a party, in an accidental warm place (for example, in a drugstore) and then must go out again to frost, you need to protect the affected area from the cold air and advise you to call a taxi: they do not save on health, but re-cooling of the newly "saved" area can lead to more severe tissue damage.
In some cases, instead of a taxi, you need to call an ambulance. The sites of frostbite of the 2nd degree should be processed by professionals in aseptic conditions, and the heavier ones require immediate hospitalization and specialized medical care. Deep cold tissue lesions, including necrosis, may not appear immediately, so if there is severe frost, prolonged hypothermia, a rapid (already frosty) bubble formation, one must suspect a heavier degree of frostbite than it seems at first glance!

 Cart
Cart