Parathyroidin (parathormone, PTG)
01 Nov 2016
Historical information
Opening of parathyroid glands usually attribute Sendstrema whose article published in 1880 passed almost unnoticed. One decade later these glands were again opened by the Gley which described consequences of their excision together with a thyroid gland. Then the Vassal and Dzhenerali showed that selective excision of parathyroid glands quickly leads to tetany, epileptic seizures and death.
Mack-Kall and Fegglin in 1909 the first described influence of paratireoektomia on concentration of a calcium in plasma. Connection between low concentration of a calcium and symptoms arising at the same time was quickly enough established, and ideas of function of parathyroid glands began to be formed. Active extracts from these glands weakened hypocalcemic tetany at the animals subjected to a paratireoectomia, and at control increased concentration of a calcium in plasma (Berman, 1924; Collip, 1925). These data for the first time allowed to bind clinical disturbances to hyperfunction of parathyroid glands.
While the American and English physiologists studied function of parathyroid glands, the German and Austrian pathologists found a fibrous and cystic ostitis in patients with tumors of these glands. Albright (Albright, 1948) in the fine historical review tracked how these two different ways succeeded to come to the identical conclusions.
Chemical properties
Molecules of paratireoidin at the person, a bull and a pig represent the one-chained polypeptides with a molecular weight about 9500 consisting of 84 amino acids. Their amino-acid sequence is completely deciphered. N-trailer sites of a chain have biological activity. And manifestations of hormonal activity are necessary the amino-acid remains with 1 on 27 for linkng with receptors. The derivatives deprived of the first or second rest though interact with receptors, but are almost not active (Aur-bach, 1988). PTG of a bull and a pig differ with seven amino-acid remains, and the N-trailer site of PTG of the person differs from the respective sites of bull and pork hormones only in four and three remains respectively. Three of these hormones have almost identical biological activity, but differ immunological.
Synthesis, secretion and methods of immunologic analysis
Parathyroidin (parathormone) is synthesized in the form of a polypeptide precursor. In the beginning it is formed so-called preproPTG, consisting of 115 amino acids. At transfer in endoplasmatic retikulum from this polypeptide 25 N-trailer amino-acid remains are split off, and it turns in PTG the Last is had to Golgi's device where from it 6 more amino-acid remains are split off. PTG which is stored in secretory granules is as a result formed and from them it is released in a blood. Normal the most part of PTG is blasted by a proteolysis even before secretion. At hypocalcemia intensity of a proteolysis decreases and cosecretes more parathormone. This mechanism allows to strengthen quickly secretion of hormone without activation of the albuminous synthesis demanding rather big time. At a long hypocalcemia also synthesis of PTG is activated that is followed by a hypertrophy of parathyroid glands. Neither preproPTG nor preproPTG don't get to a blood. Synthesis and processing of a parathyroidin are in detail described, for example, in the review of Kgonenberg of all. (1994).
T1/2 of a mature parathormone in plasma makes 2 5 min.; its elimination approximately for 90% is carried out by a liver and kidneys At disintegration of PTG the fragments continuing to circulate in a blood are formed. A part of fragments is formed also in parathyroid glands at PTG proteolysis. Fragments have no biological activity, but react with antibodies to PTG. Nevertheless there are immunologic methods of definition of PTG, rather reliable for the clinical purposes. RIA with use of two types monoclonl the nykh of antibodies (one to N-trailer, and another to the S-trailer site of a molecule) has high sensitivity and allows to define the maintenance of mature PTG precisely. This method is used instead of old options of RIA now (Nus-sbaum and Potts, 1994).
Physiology
PTG main function ensuring constancy of concentration of calcium in blood. Paratireoidin (paratgormon) influences absorption of calcium in intestines, mobilization of calcium from a bone tissue, a calcium ekskretion with urine, a stake, then and milk. Action of PTG on fabric target is mediated by the membrane receptor interfaced to G-protein (hl. 2). Methods of cloning have established the amino-acid sequence of a receptor and an arrangement of seven of his transmembrane domains (Juppner et al., 1991).
Regulation of secretion
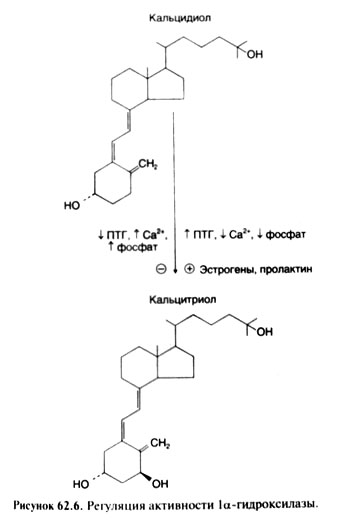
The most potent regulator of activity of parathyroid gland is concentration of the ionized calcium in plasma. At its low concentration secretion of PTG increases and if hypocalcemia remains a long time, the hypertrophy and a hyperplasia of parathyroid glands develops. At high concentration secretion of PTG decreases. The researches in vitro showed that low concentration of the ionized calcium in medium for a long time stimulates transport of amino acids in cells of parathyroid glands, synthesis of nucleic acids and protein in them, conducts to augmentation of volume of cytoplasma and intensifying of secretion of PTG. High concentration of a calcium has opposite effect. Thus, a calcium immediately regulates a condition of parathyroid glands, as well as synthesis and secretion of PTG.
Fluctuations of concentration of the ionized calcium in a blood are perceived by the specific membranous receptor located on a surface of cells of parathyroid glands (Brown et al., 1993). Linkng of a calcium with a receptor suppresses secretion of PTG. Hypercalcemia leads to depression of intracellular maintenance of tsAMF and activity of protein, and hypocalcemia activates this enzyme. However communication between these changes and shifts in secretion of PTG is found out not up to the end. Other factors which increase the maintenance of tsAMF in cells of parathyroid glands (for example, p-adrenostimulyatory and Dofaminum) also stimulate secretion of PTG, but in much smaller degree, than hypocalcemia. The active metabolite of vitamin D calcitriol suppresses PTG gene expression. Fluctuations of level of Natrii phosphas in a blood in the physiological range, apparently, don't influence secretion of PTG (if, certainly, these fluctuations don't lead to essential changes of concentration of the ionized calcium). At expressed hyper-and hypomagnesiemia secretion of PTG can decrease (Rude et al., 1976).
Thus, concentration of a calcium in a blood is regulated on a feedback mechanism: the regulatory system perceives the level of the ionized calcium in a blood, and in response to it secretion of PTG changes; the last affects various target tissues, enlarging entering of a calcium in a blood.
Influence on bones
Parathyroidin (parathormone) enlarges entering of a calcium from bones in a blood, accelerating process of resorption of a bone tissue during which both organic, and mineral components of intercellular substance are released. PTG cells targets in bones are probably osteoblasts. PTG receptors on osteoclasts are found only in birds. For lack of other cells of PTG doesn't enlarge activity of the osteoclasts applied on a bone surface. Reaction to hormone appears if osteoclasts are cultivated in medium in which there were osteoblasts treated to action PTG before. It testifies to an important role of osteoblasts in stimulation of a resorption of a bone tissue under the influence of PTG (McSheehy and Chambers, 1986; Perry et al., 1987; Takanashi et al., 1988).
Under the influence of PTG precursors of osteoclasts form new units of osteal updating. At long rising of the PTG level there are characteristic histological changes in bones: the number of the centers of a resorption and, respectively, an area of the osteal surface covered with not mineralized organic matrix is enlarged. In this case it indicates not disturbance of a mineralization, and total magnification of the area of bone formation owing to activation of processes of updating of a bone. You can also like Phenazepam.
At PTG incubation with the isolated osteoblasts it usually suppresses their function: decrease formation of collagen I of type, alkaline phosphatase and osteokaltsin. However action of PTG in vivo includes not only influence on separate cells, but also augmentation of total of active osteoblasts as there are new units of osteal updating. As a result the level of an osteokaltsin and activity of an alkaline phosphatase can increase in plasma. Simple model which completely would explain the molecular mechanism of action of PTG on a bone tissue, doesn't exist. The parathyroidin (parathormone) stimulates formation of tsAMF in osteoblasts, but there are data and on a role of an intracellular calcium in oposredon of some effects of this hormone.
Influence on kidneys
In kidneys of PTG has double effect. First, it strengthens reabsorption of calcium and suppresses a phosphate reabsorption; it leads to increase in concentration in blood of calcium and to decrease phosphate. Secondly, PTG stimulates transformation of vitamin D into its active form calcitriol (see below). The last contacts receptors in intestines and stimulates calcium absorption that also promotes increase in concentration of calcium in blood. Influence on calcium exchange. PTG strengthens calcium reabsorption in disteel departments of nefron (Agus et al., 1973). Removal of parathyroid glands in case of initially normal concentration of calcium in plasma leads to decrease in its canal reabsorption and by that to increase in its ekskretion with urine. When concentration of this ion in plasma falls lower than 7 mg of % (1,75 mmol/l), its ekskretion decreases: the amount of calcium filtered in balls is so small that it almost reabsorb completely, despite a reduced reabsorb capability of tubules. When entering PTG animal or to the person with canal reabsorption of calcium increases, and the ekskretion decreases. Along with intake of calcium from bones and strengthening of its absorption in intestines it leads to increase in concentration of calcium in blood. When it appears above a regulation, the amount of the filtered calcium begins to exceed possibilities of canal reabsorption (even strengthened under the influence of PTG) and there is a hypercalcium.
Influence on exchange of phosphate
Paratireoidin (paratgormon) increases a kidney ekskretion of phosphate due to decrease in its reabsorption therefore the hypofosfatemia is characteristic of hyperparatireoz.
Action of PTG on kidneys is mediated by tsAMF (Aurbach, 1988). Its activity increases under the influence of PTG is found in cells of cortical substance of kidneys. It leads to strengthening of synthesis of tsAMF which influences canal reabsorption. A part of tsAMF from cages of tubules gets to urine therefore on content of tsAMF in urine judge activity of parathyroid glands and sensitivity of kidneys to PTG. Influence on exchange of other ions. PTG reduces a kidney ekskretion of magnesium, increasing its reabsorption, and strengthens its mobilization from a bone tissue (MacIntyre et al., 1963). Paratireoidin (paratgormon) raises a kidney ekskretion of water, amino acids, citrate, K+, bicarbonate, Na+, SG and SOj ~, but brakes H+ ekskretion. Influence of PTG on a kidney ekskretion of acids and the bases is similar to effect of acetazoleamide, however it isn't mediated by influence on carboangidrasa.
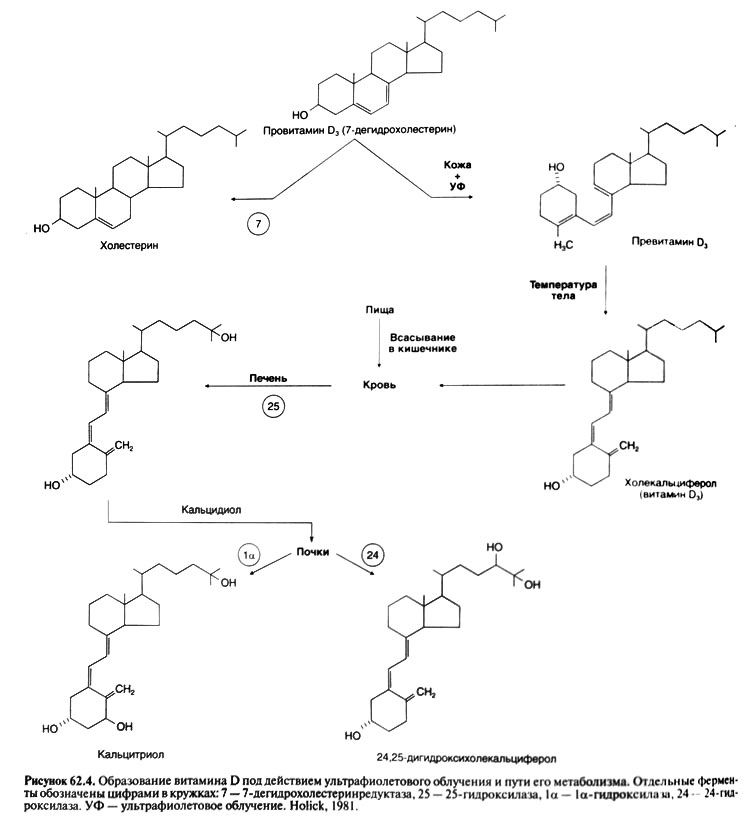
Influence on synthesis of calcitriol
In cells of a renal canaliculus the final stage of activation of vitamin D its transformation into a hormonal form, that is into calcitriol is carried out (see below). Activity of the la-hydroxylase catalyzing this transformation is regulated by three major factors: Natrii phosphas, PTG and calcium. Depression of concentration of Natrii phosphas in a blood or tissues quickly enlarges formation of calcitriol. A potent stimulator of formation of calcitriol is also PTG whereas hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia suppress this process. Thus, when hypocalcemia leads to rising of secretion of PTG, concentration of calcitriol increases in a blood not only because of PTG - dependent depression of concentration of Natrii phosphas, but also owing to direct influence of hormone on activity of a 1a-hydroxylase.
Other effects
Parathyroidin (parathormone) reduces concentration of a calcium in milk and saliva, despite simultaneous rising of its concentration in plasma. Thus, constancy of concentration of a calcium in a blood is provided with also inhibiting influence of PTG on transport of this cation in milk and saliva.
General scheme of a regulation of concentration of a calcium in a blood. Reaction of cells of parathyroid glands even on small depression of concentration of the ionized calcium arises very quickly (within minutes). Correction of short-term fluctuations of concentration of a calcium in a blood is provided with influences of PTG on a calcium reabsorption in kidneys. At longer hypocalcemia in kidneys the 1a-hydroxylase is activated that leads to augmentation of formation of calcitriol; the last stimulates a calcium absorption in an intestine. Besides, a calcium from labile fraction of bones comes to a blood. At a long and serious hypocalcemia processes of updating of bones accelerate (the quantity of units of osteal updating increases); it also leads to a calcium exit in a blood, but already due to depression of mass of a bone tissue.
When concentration of the ionized calcium in plasma is enlarged, secretion of PTG falls and the canalicular reabsorption of a calcium decreases. Besides, depression of the PTG level in a blood promotes Natrii phosphas reabsorption in kidneys. Both depression of the PTG level in itself, and a hyperphosphatemia suppress formation of calcitriol that, in turn, leads to decrease of an absorption of a calcium in an intestine. At last, also process of updating of bones is slowed down.
The scheme of a regulation of concentration of a calcium in a blood is provided. It is visible that 2 hormones (PTG and calcitriol) and 3 effector organs participate in this regulation (kidneys, a GIT and bones). In the provided scheme the role of other hormones isn't considered (for example, a calcitonin), but at the person they, most likely, don't regulate concentration of a calcium in a blood independently, and only modulate activity of the main regulatory system including PTG and vitamin D.
Hypoparathyrosis
This quite infrequent state which is only one of many reasons of hypocalcemia (see above). Most often the hypoparathyrosis arises after operations on thyroid or parathyroid glands. More rare he is is caused by genetic or autoimmune disorders. At pseudohypoparathyroidism biochemical disturbances same as at a hypoparathyrosis, but the PTG level in a blood is increased This state it is caused by resistance of target organs to PTG usually owing to defect of a receptor, G-protein or adenylatecyclase (Levine, 1999).
Both at hypoparathyrosis, and at pseudohypoparathyroidism the hypocalcemia and symptoms accompanying it are observed. The earliest symptom of hypocalcemia is paresthesia in extremities. The percussion a hammer on nerves causes reduction of the corresponding sceletal muscles (for example, Hvostek's symptom reduction of face muscles in response to blow by a hammer on a point of an exit of a facial nerve). After this the tetany tonic cramps of muscles can develop (especially cramps of muscles of brushes and feet and laryngospasm). At last, there are generalized epileptic seizures and other central disturbances. Symptoms from smooth muscle organs are possible spastic strictures of a ciliary muscle (an accommodation spastic stricture), muscles of an iris, esophagus, intestine, a bladder and bronchi. Changes of an ECG and the expressed tachycardia testify to a heart lesion. Often there are vasospasms of fingers of arms and legs. At chronic hypoparathyrosis changes of tissues of ectodermal parentage meet: hair loss, lamination and fragility of fingernails, defects of an adamantine substance of tooth and cataract; at roentgenography of the head it is possible to find a calcification of basal kernels. Quite often there are mental symptoms: emotional lability, alarm, depression and delirium.
Apply to treatment of hypoparathyrosis and pseudohypoparathyroidism mainly vitamin D (see below). Also calcium additives can be required.
Hyperparatireos
Primary hyperparatireos is caused by hyper secretion of PTG one or several parashitovidny glands. Concentration of calcium in plasma in case of hyperparatireos sometimes remains normal, but is usually increased. Concentration of phosphate is on the lower bound of a regulation or is reduced. Ekskretion of calcium with urine, as a rule, increases, reflecting prevalence of its filtering over canal reabsorption (even strengthened under the influence of PTG). However the calcium ekskretion in case of hyperparatireos nevertheless is less, than in case of hyperkaltsiyemiya of other origin (in case of identical concentration of calcium in plasma). Secondary hyperparatireos develops as compensatory reaction to decrease in level of calcium in blood and isn't followed by a giperkaltsiyemiya. At the same time concentration of phosphate is especially small (if only at the same time there is no renal failure), and activity of alkaline phosphatase in serum is sharply increased.
In case of heavy primary or secondary hyperparatireos special damage of bones is fibrous and cystous osteitis can be observed. However at most of patients with primary hyperparatireos of change of bones are expressed very poorly. Usually they include moderate decrease in general density of a bone tissue at the expense of compact substance; density of spongy substance decreases a little (Bilezikian et al., 1994).
Diagnostics of hyperparatireos was simplified by emergence of methods of RIA allowing to determine the level of mature PTG. The hypercaltsiemia combination to the increased level of mature PTG allows to make the correct diagnosis more than in 90% of cases.
Treatment
Removal of single adenoma of a parathyroid gland (about 80% of cases of hyperparatireos) either removal or subtotal resection of several hyperplasirglands (about 15% of cases of hyperparatireos), carried out by the experienced surgeon, leads to treatment of hyperparatireos. The passing postoperative hypocaltsiemia can be connected with temporary violation of blood supply of the remained ferruterous fabric or with the strengthened calcium absorption by a bone tissue. Fixed hyperparatireos, requiring lifelong treatment by vitamin D and calcic additives a heavy, but rare complication of transactions on parathyroid glands.
Use of PTG
In last PTG applied to rising of concentration of calcium in plasma, however the same effect with larger safety can be reached administration of calcium and vitamin D. In the list of the resolved FDA of PTG remedies is absent, but use of PTG or its analogs can be approved at an osteoporosis in the near future. It is shown that daily introduction of PTG(134) sick with an osteoporosis considerably enlarges the mass of a bone tissue of a backbone (see. "Osteoporosis"). PTG(134) can be used for differential diagnostics of hypoparathyrosis and pseudohypoparathyroidism. As resistance of target organs to PTG is characteristic of pseudohypoparathyroidism, administration of drug doesn't raise tsAMF egestion with urine. This assay allows to tap the nature of disturbances at certain patients and their relatives, however the diagnosis is usually established by determination of level of mature PTG in plasma.

 Cart
Cart