DMAA
25 Nov 2016
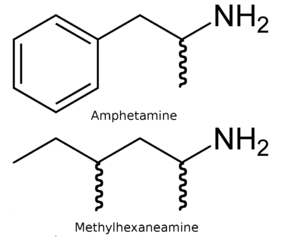
DMAA, 1.3 dimethylamylamin (is also known as 1.3 dimethylpentylamin, methylhexaneamin, 2-amino-4-methylhexan, geranamin) is a monoamine with the stimulating and euphoric action, similar in action to caffeine. In a brain 1.3 dimethylamylamin influences mood and emotions, increases mental concentration. It is connected with increase in concentration of dopamine and noradrenalin in intersynaptic spaces. DMAA is considered from four to ten times stronger, than caffeine, at the same time without causing toxicity and harm for an organism. Often joins in sports food for performance improvement and combustion of fat. Metilgeksanamin was for the first time issued by DMAA under a trade name of Forthane and was made by the Eli Lilly & Co company. As vasoexcitor (vasoconstrictive agent) in the 1940th years. After several decades of obscurity, since 2006 Proviant Technologies under a trade name geratamin began issuing and it was applied in the field of sport as dietary additive in pretraining complexes and fat loss. It became possible, after a release of the scientific article of Journal of Guizhou Institute of Technology where geratamin was provided as the natural product extracted from a geranium (Pelargonium graveolens).
Prohibition
In 2009 methylhexaneamin was added to the list of the forbidden substances of world anti-doping agency (WADA) and ranked as group of stimulators. In 2010 and 2011 some athletes were disqualified and deprived of awards in different types of sport, because of detection in DMAA blood. As of 2013 remains easily available in the market of sports food.
As of the beginning 2013 of DMAA practically disappeared from structure of the majority of the known brands. Many producers, including Primaforce suspended production or excluded methylhexaneamin from structure. However in 2015-2016 new additives which main active ingredient is DMAA in large quantities began to be issued.
Legal legality
DMAA is legislatively forbidden in some western countries. Are basic reasons of a prohibition: the most powerful impact on TsNS, "explosive" stimulation of various systems, weak study of consequences and the uncontrolled acceptance attracting insignificant probability of emergence of functional violations.
In the Russian Federation 1.3 dimethylamylamin is legal and readily available substance with low cost.
DMAA in sports food
In 2011 American Herbal Products Association (AHPA) declared that producers of additives shan't specify on packagings and in instructions methylhexaneamin as oil of a geranium (geranium oil) or other component of this plant to exclude unintentional acceptance on ignorance. This offer was supported by United Natural Products Alliance (UNPA) in January, 2012. Thus, if you purchase additive, then now in structure you will be able to find the following names: 1.3 dimethylamylamin (DMAA), methylhexaneamin or geranamin. The last name is used most often in sports food. Do not forget take Zhenoluten for better results.
"Attention" the Average dosage fluctuates from 15 to 200 mg. It isn't recommended to accept a dose more than 75 mg.
Content of DMAA in sports food.
Origin
Still remains not clear whether receive 1.3 dimethylamylamin for sports additives from a plant or use synthetic. Including it is urgent for such popular additives as Jack3d and OxyElite whereas the producer specifies that geranamin is received from a geranium. With respect thereto the research during which researches by methods of gas hromatomass-spectrometry (GC-MS) and a liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry of high resolution (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS) which allowed to conclude that the geranium oil received by steam distillation from various parts (flowers, stalks, leaves) of a plant of Pelargonium graveolens doesn't contain geranamin (≥10 ppb) were conducted was initiated, and sports additives are enriched with synthetic DMAA.
Other research showed methylhexaneamin doesn't contain (> 2ppb) not only in geranium oil, but even in various parts of the fresh and dried-up plant.
Effects
- The expressed psychophysical stimulation
- Increase in working capacity
- Improvement of mood
- Strengthening of lipoliz (combustion of fat)
- Appetite suppression
Effect of methylhexaneamin exponentiates other stimulators, including caffeine sodium benzoate.
Side effects and harm
From the most often meeting it is possible to mark out the following side effects:
- Shiver
- Sweating
- Hyperthermia
- Sleeplessness
- Nausea
- Headache
- Rising of arterial pressure, tachycardia, stroke (at appreciable excess of the recommended dose)
- Dryness in a mouth
Harm and safety of use of DMAA in additives is quite discussed question. Cases when methylhexaneamin caused serious collateral reactions were repeatedly recorded. So in December, 2010, Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association published data on the 21-year-old man with the developed hemorrhage after reception of geranamin together with a large amount of alcohol. [12] In December, 2011, it was reported about two fatal cases among soldiers of the USA that it was bound to the use of the additive containing dimethylamylamin.
In view of the fact that methylhexaneamin is considered as a natural vegetable component, products the containing extracts or oil of a geranium FDA aren't regulated and are ranked as group of dietary supplements. However articles published in 1951[14] and 1960 years, also as well as National Cancer Institute (NCI) at a research of action of synthetic DMAA showed that development of side effects and toxicity is possible.
Despite special cases and fears of experts, in many respects danger of additive it is exaggerated, and development of collateral reactions is most often bound to an over dosage, a combination to other stimulators (caffeine) and disturbance of prescriptions on reception. Several researches which confirm safety for healthy people at the use according to the recommended scheme are executed.
Objective research of safety
The lethal dose for mice (LD50) makes 39 mg/kg intravenously and 185 mg/kg intraperitoneal. What does people say about low toxicity of DMAA?
In September, 2011 these researches in which consuming 1.3 dimethylamylamin in a dose of 75 mg ("solo" and in case of a combination to caffeine) was caused by increase in arterial pressure above a norm were published. At the same time the health remained satisfactory, pulse rate didn't increase.
Careful observation over 25 healthy men in 2012 accepting geranamib the containing pretraining Jack3d complex (USP Labs) allowed to define that substance doesn't exert the considerable impact on pulse rate, arterial pressure, doesn't influence a status of a liver and kidneys when it is used in the recommended doses. [According to a row of additional operations, DMAA doesn't render serious harm on an organism.
Doping testing
As a rule it doesn't enter standard doping tests, however can be defined by method of a liquid chromatography in urine samples. According to Analytical Chem Insights[21] after reception of a dose of 40 mg time of detection 1,3-DMAA reaches 105 hours. The method of the forced dieresis allows accelerating deduction.
For the last 3 years the positive doping tests at dozens of athletes from different disciplines were revealed:
- hockey (Anton Belov, Vitaly Pavlov)
- boxing (Brandon Ríos)
- biathlon (Evie Zahenbaher-Stehle)
- cross-country skiing (Marit Bjørgen)
- run (Gufran Almukhamad)

 Cart
Cart