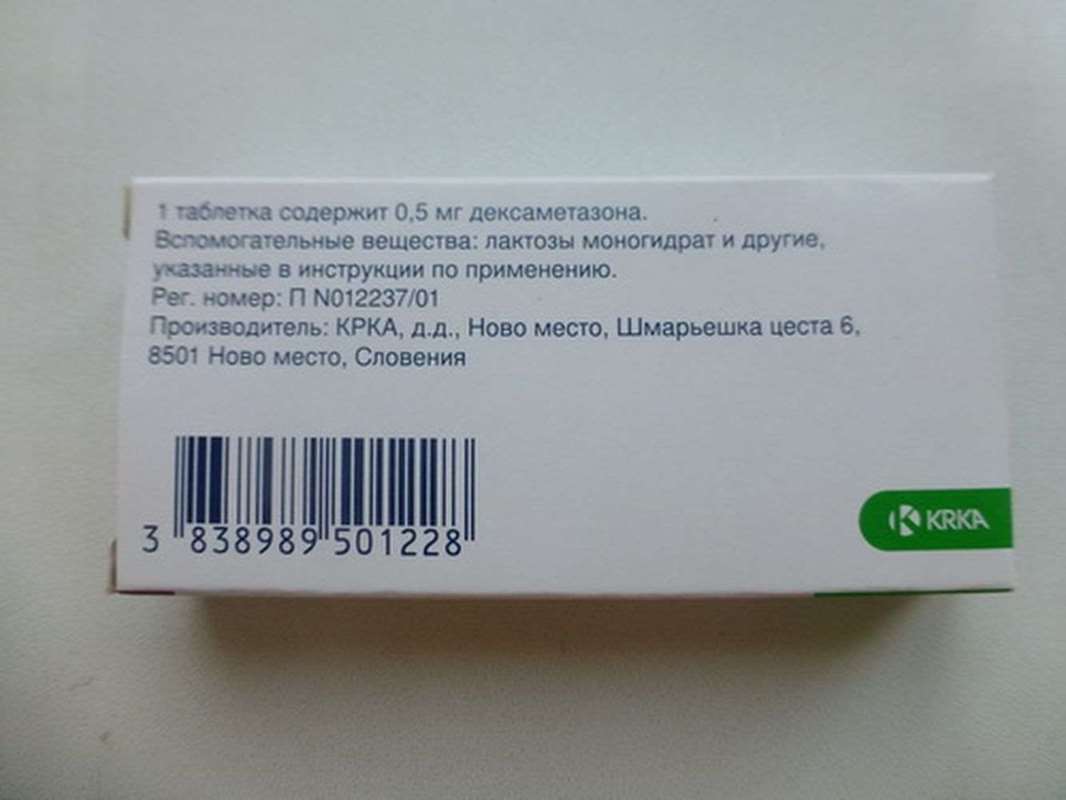
Dexamethasone (Dexamethasonum, Dexamethasoni) - drug, synthetic glucocorticosteroid having immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory action coupled with the ability to penetrate the CNS. Because of these properties can be used in the treatment of brain edema and inflammatory eye diseases (including in combination with tobramycin). Dexamethasone in the form of tablets and solution for injection is included in the list of vital and essential medicines.
Has anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, desensitizing, immunosuppressive, antishock and antitoxic action, increases the sensitivity of the beta-adrenergic receptors to endogenous catecholamines. Interacts with specific cytoplasmic receptors (receptors for glucocorticosteroids have all tissues, many of them especially in the liver) to form a complex formation-inducing proteins (including enzymes, to regulate vital cell processes).
Mode of action - glucocorticoid, an anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antishock, immunosuppressive.
It interacts with specific cytoplasmic receptors and form a complex that penetrates the cell nucleus; depression or induces expression of mRNA on ribosomes changing the formation of proteins, including lipocortin mediating cellular effects. Lipokortin inhibits the A2 phospholipase, liberatiou suppresses arachidonic acid inhibits the biosynthesis endoperekisey, PG, leukotrienes that promote inflammation, allergies and others. It prevents the release of inflammatory mediators from eosinophils and mast cells. It stops the activity of hyaluronidase, collagenase and proteases, normalizes the function of the extracellular matrix of cartilage and bone. Reduces capillary permeability, stabilizes cell membranes, including lysosomal inhibits the release of cytokines (interleukins 1 and 2, gamma interferon) of lymphocytes and macrophages. Affects all phases of inflammation, anti-proliferative effect is due to inhibition of monocyte migration into the inflammatory focus and fibroblast proliferation. Causes of lymphoid tissue involution and lymphopenia, which causes immunosuppression. In addition to reducing the number of T cells reduced their effect on B cells and immunoglobulin production is inhibited. The effect on the complement system is to reduce the formation and improvement of the collapse of its components. Antiallergic action is a consequence of inhibition of synthesis and secretion of mediators of allergy and reducing the number of basophils. Restores adrenoceptor sensitivity to catecholamines. It accelerates the catabolism of proteins and reduces their content in the plasma, decreases glucose utilization by peripheral tissues and gluconeogenesis in the liver increases. It stimulates the formation of enzyme protein in the liver, surfactant, fibrinogen, erythropoietin lipomodulina. It is redistribution of body fat (adipose tissue lipolysis increases limbs and the deposition of fat in the upper half of the body and face). It favors the formation of higher fatty acids and triglycerides. It reduces absorption and increases excretion of calcium; delay sodium and water secretion of ACTH. It has protivoshokovym action.
Once inside quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, Tmax -. 1-2 hours in the blood is associated (60-70%) with a specific transporter protein - transcortin. Easily it passes through the blood-tissue barriers, including GEB and placenta. Biotransformed in the liver (mainly by conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfuric acid) to inactive metabolites. T1 / 2 of plasma - 3-4.5 h, T1 / 2 of fabric -. 36-54 hours excreted by the kidneys and through the intestine passes into breast milk.
After instillation in the conjunctival sac penetrates well into the epithelium of the cornea and conjunctiva, while in the aqueous humor of the eye are therapeutic concentrations of drugs. When inflammation or damage to mucosal penetration rate increases.
Indications:
Diseases that require a rapid-SCS, as well as cases when oral administration of the drug can not be:
- Endocrine diseases: acute adrenal insufficiency, primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, subacute thyroiditis;
- Shock (Burn, traumatic, operational, toxic) - the ineffectiveness vasoconstrictor, plasma-drugs and other symptomatic therapy;
- Swelling of the brain (with brain tumors, head trauma, neurosurgical intervention, stroke, encephalitis, meningitis, radiation injury);
- Status asthmaticus; severe bronchospasm (exacerbation of asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis);
- Severe allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock;
- Rheumatic diseases;
- Systemic disease of the connective tissue;
- Acute severe dermatoses;
- Malignant diseases: palliative treatment of leukemia and lymphomas in adults; acute leukemia in children; hypercalcemia in patients with malignant tumors, failing oral treatment;
- Blood disorders: acute hemolytic anemia, agranulocytosis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults;
- Severe infectious disease (in conjunction with antibiotics);
- In ophthalmic practice (subkonnktivalnoe, retrobulbar or parabulbarno introduction): allergic conjunctivitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis without epithelial damage, iritis, iridocyclitis, blepharitis, Blepharoconjunctivitis, scleritis, episcleritis, inflammation after eye injuries and surgical interventions, sympathetic ophthalmia, immunosuppressive treatment after corneal transplants;
- Local application (to the pathological formation): keloids, discoid lupus erythematosus, granuloma annulare.
Side effect:
Dexamethasone usually well tolerated. It has low mineralocorticoid activity, i.e. its effect on water and electrolyte metabolism is low. Typically, the low and medium dose Dexamethasone did not cause the delay of sodium and water in the body, increased excretion of potassium. We describe the following side effects:
From endocrine system: reduction of glucose tolerance, steroid diabetes or a manifestation of latent diabetes mellitus, adrenal suppression, Cushing's syndrome (moon face, obesity, pituitary type, hirsutism, increased blood pressure, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, muscle weakness, striae) , delayed sexual development in children.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, pancreatitis, steroid stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers, erosive esophagitis, gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation of the wall of the gastrointestinal tract, increased or decreased appetite, indigestion, flatulence, hiccups. In rare cases - increase in liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase.
Cardio-vascular system: arrhythmia, bradycardia (up to cardiac arrest); development (in predisposed patients) or increased severity of heart failure, electrocardiographic changes typical of hypokalemia, increased blood pressure, hypercoagulation, thrombosis. Patients with acute and subacute myocardial infarction - the spread necrosis, slowing the formation of scar tissue, which can lead to rupture of the heart muscle.
From the nervous system: delirium, disorientation, euphoria, hallucinations, manic-depressive psychosis, depression, paranoia, increased intracranial pressure, nervousness or anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, vertigo, pseudotumor cerebellum, headache, convulsions.
From the senses: posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased intraocular pressure with possible damage to the optic nerve, the propensity to develop secondary bacterial, fungal or viral eye infections, trophic changes of the cornea, exophthalmos, sudden loss of vision (for parenteral administration in the area of the head, neck, nose shells, the scalp may be the deposition of crystals of the drug in the blood vessels of the eye).
On the part of metabolism: increased excretion of calcium, hypocalcemia, increased body weight, negative nitrogen balance (increased protein breakdown), increased sweating.
Conditional mineralocorticoid activity - fluid and sodium retention (peripheral edema), gipsrnatrnemiya, gipokaliemncheskiysindrom (hypokalemia, arrhythmia, myalgia or muscle spasm, unusual weakness and fatigue).
From the musculoskeletal system: slowing growth and ossification in children (premature closure of epiphyseal growth zones), osteoporosis (very rare - pathological fractures, aseptic necrosis of the humeral head and femur), rupture of tendons of muscles, steroid myopathy, reduced muscle mass (atrophy).
For the skin and mucous membranes: delayed wound healing, petechiae, ecchymosis, thinning of the skin, hyper- or hypopigmentation, steroid acne, striae, susceptibility to the development of pyoderma and candidiasis.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, pruritus, anaphylactic shock, local allergic reactions.
Local when administered parenterally: burning, numbness, pain, tingling in the introduction, infection at the injection site, rarely - necrosis of surrounding tissue, scarring at the injection site; atrophy of the skin and subcutaneous tissue with the / m introduction (especially dangerous administration in the deltoid muscle).
Other: development or exacerbation of infection (the appearance of this side effect contribute jointly used immunosuppressants and vaccination), leucocyturia, "tides" of blood to the face, "cancellation" syndrome.
Suggested Use:
Dosage is individual and depends on the indication, the patient's condition and response to therapy. The drug is injected in / in the slow jet or drip (for acute and urgent conditions); / m; it is also possible locally (in the pathological formation) administration. In order to prepare the solution for I / drip infusion to be used isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution.
In the acute period in various diseases and early therapy Dexamethasone used in higher doses. During the day may be administered from 4 to 20 mg Dexamethasone 3-4.
Doses for children (w / o):
Dose in replacement therapy (for adrenocortical insufficiency) is 0.0233 mg / kg or 0.67 mg / m2 of body surface area, divided into 3 doses every third day or 0.00776 - 0.01165 mg / kg body weight or 0.233 - 0.335 mg / m2 body surface area daily. For other indications the recommended dose is from 0.02776 to 0.16665 mg / kg body weight or 0.833 - 5 mg / m2 body surface every 12-24 hours.
Upon reaching effect reduce the dose to maintenance or to discontinuation of treatment. Duration of parenteral use is usually 3-4 days, then move on to maintenance therapy with dexamethasone tablets.
Long-term use of high doses of the drug requires a gradual reduction of the dose to prevent the development of acute adrenal insufficiency.
Packaging:
- Comes in original packaging. Item is brand new and unopened.
Storage:
- Keep away from direct sunlight.
- Keep locked and away from children.
- Store in dry place at room temperature.
- Do not exceed storage temperature higher than 25 C
Important notice - the outer box design may vary before prior notice!

 Cart
Cart