Riboflavin - Active Substances. Instruction and Application, Dosage
26 Dec 2016
Name: Riboflavin
The Latin name of the substance Riboflavin
Riboflavinum (genus Riboflavini)
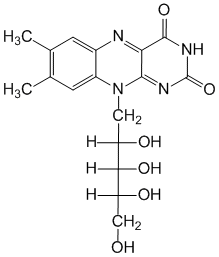
Chemical name: 7,8-Dimethyl-10- (D-ribitol-1) isoalloxazine (in the form of sodium monophosphate)
Formula - C17H20N4O6
Therapeutic substances Riboflavin- Vitamins and vitamin-like agent
The nosological classification (ICD-10)
B15 Acute hepatitis A
B37 Candidiasis
E46 Protein-energy malnutrition, unspecified
E53.0Riboflavin deficiency
H10.9 Conjunctivitis, unspecified
H16 Keratitis
H17 Corneal scars and opacities
H20 Iridocyclitis
H25 Senile cataract
H26 Other cataract
H53.1 Subjective visual disturbances
K12 Stomatitis and related lesions
K13.0 Diseases of lips
K13.7 Other and unspecified lesions of oral mucosa
K14.0glossitis
K73 Chronic hepatitis, not elsewhere classified
K74 fibrosis and cirrhosis
K90 Disorders of absorption in the intestine
L20 Atopic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis
L21L30.9 Dermatitis, unspecified
L56 Other acute skin changes caused by ultraviolet radiation
L71 Rosacea
L98.4 Chronic ulcer of skin, not elsewhere classified
R53 Malaise and fatigue
T14.1 Open wound of unspecified body region
T66 Unspecified effects of radiation
CAS code - 83-88-5
Characteristics substance Riboflavin
Vitamin B2. Yellow-orange crystalline powder bitter taste, with low specific smell, the light is unstable. It is soluble in water and alcohol. Aqueous solutions are yellowish in color.
PharmacologyMode of action -, the lack of vitamin B2, regulates redox processes.
Substrate activates the synthesis of flavin co-enzymes, interacts with the ATP forms a flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide, involved in the transport of protons and regulation of redox processes. Chemically pure riboflavin and nucleotides are rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, slowing the absorption of various inflammatory processes in the intestine, poor circulation, Akhil, chronic gastritis, enteritis; in infants absorption is slower than in adults. Uneven distribution in the body: the greatest quantity detected in the myocardium, liver and kidneys. Provided mainly with urine in an unmodified form; with normal vitamin in the body in the urine per day for around 9% of the administered dose, and the rest is reabsorbed in the tubules of the kidneys; excessive addition increases the excretion of urine and turns yellow. Elimination of riboflavin increased in thyrotoxicosis.
Plays an important role in metabolism, is involved in the processes of growth. The daily requirement for adults is 2.5 mg, with heavy physical labor - about 3 mg; for children from 6 months to 1 year - 0.6 mg, 1-1.5 years - 1.1 mg, from 1.5-2 years - 1.2 mg, 3-4 years - 1.4 mg, 5 -6 years - 1.6 mg, 7-10 years - 1.9 mg, 11-13 years - 2.3 mg, 14-17 years: for boys - 2.5 mg for women - 2.2 mg.
It supports phagocytosis process influences the morphology and function of the central and autonomic nervous systems, plays an important role in maintaining normal visual function of the eye and in the synthesis of erythropoietin, hemoglobin. Several increases gastric secretory function (involved in the formation of hydrochloric acid of the gastric juice), improves biliary excretion, facilitates the absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine, is necessary for the maintenance of normal intestinal microflora. Improves Glycogen-fixing, synthetic, anti-toxic liver function, increases the sensitivity of liver cells to insulin, promotes insulin incretion. It normalizes blood bilirubin (hepatitis A).
Application of the substance Riboflavin
Hypo- and ariboflavinoz exogenous and endogenous origin, day-blindness, conjunctivitis, iritis, keratitis, corneal opacities, cataracts, long-term healing wounds and ulcers, radiation sickness, asthenia, cheilitis, angular stomatitis (perleches), glossitis, itching dermatosis, eczema, neurodermatitis, photodermatosis, seborrhea, rosacea, candidiasis, viral hepatitis A, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract function, sprue, malnutrition, anemia, leukemia. As a preventive measure - reduced absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, and increase the intensive elimination of the need for riboflavin (acute and chronic hypoxia, respiratory and cardiac failure, burn disease, frostbite, lack of protein and carbohydrate supply redundancy, acute infectious diseases, including the treatment of antimicrobial agents that suppress gram-negative intestinal flora, phototherapy).
Side effects of Riboflavin substance
Visual impairment, renal function, and allergic reactions.
Interaction
Chlorpromazine, imipramine, amitriptyline violate (flavinokinazy block) including riboflavin flavin mononucleotide, flavin adenine dinucleotide and increase its excretion in the urine. The combined application with accelerates the metabolism of thyroid hormones. Under the influence of m-choline blockers increase the absorption and bioavailability (due to slow bowel movement). Compatible with antianemic means antihypoxants, anabolics. It prevents or reduces the adverse effects of chloramphenicol (impaired hematopoiesis, optic neuritis). Perhaps the decline in the activity of the tetracyclines.
Dosing and Administration of Riboflavin
Inside - 5-10 mg (children - 2-5 mg) 1-3 times a day for 1-1.5 months. The daily dose - 50 mg.
V / m - 1 ml of a 1% solution of 1 times a day for 10-15 days (children - 3.5 days), then 2-3 times a week, total - 15-20 injections. With eye diseases - by 0.2-0.5 ml of a 1% solution in 10-15 days.
Precautions for Riboflavin substance Perhaps staining of urine yellow..
Trading names of drugs with Riboflavin working substance
Trade Name Index
Vitamin B2, Riboflavin, Riboflavin 100 High Flow, sodium riboflavin-5-phosphate, Riboflavin mononukleotid

 Cart
Cart