Norepinephrine (Noradrenalinum)
22 Oct 2016
Physiologist says about the inventing of Adrenaline, noradrenaline and pharmacological studies of its effects on behavior.
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are easily confused: similar names and chemical formulas, both of them are associated with stress and excitement, both open in the adrenal glands. However adrenaline is a hormone, norepinephrine its mainly functions as a mediator of the nervous system.
"Hormone" means that the substance is released into the blood special cells are often assembled in iron. Hormones are distributed throughout the body, acting on many organs and tissues, and their effects last for a long time - minutes and hours. Mediators released from the process of neuron (axon), forming contact with the target cell - muscular, glandular, another neuron. The mediator acts pointwise only on the cell, altering its activity is not more than a few seconds.
Adrenaline was isolated at the end of the XIX century, and immediately began to actively explore and use in clinical practice. Later, it was discovered norepinephrine. The classic work on their study carried out under the leadership of Englishman Henry Dale - one of the founders of modern pharmacology. In 1936, Dale received the Nobel Prize for the discovery and description of the mechanisms of chemical transmission of signals in the nervous system.
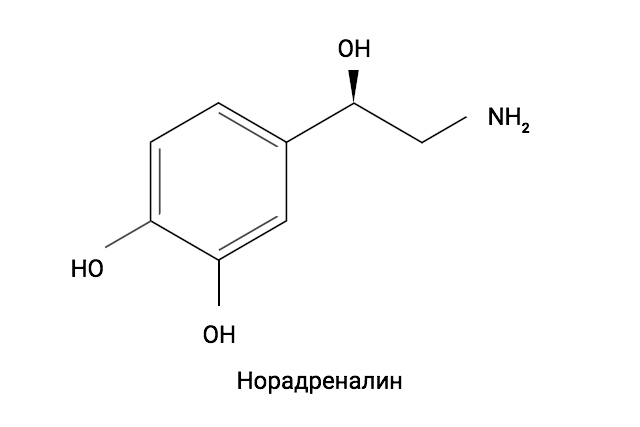
Conversion and Action of Noradrenaline
As adrenaline and noradrenaline in the body formed from tyrosine. Tyrosine - one of the 20 amino acids comprising the protein foods. Every day with the different foods we consume several grams of tyrosine, able to turn into norepinephrine, and then in the adrenal glands in the adrenaline. Foods rich in tyrosine, and derivatives thereof, the nervous system and activates many organs. In this regard, for example, acute cheese varieties have not advisable at night (or, say, antidepressants).
Contact axon of a neuron cell to the next, which operate neurotransmitters including noradrenaline, called a synapse. The operation of the synapse occurs when the axon comes to an electrical impulse that signals the importance of sensory stimulus, such as pain, emotions, decisions taken by the brain. Mark the end of the axon, the mediator acts on receptors - sensitive proteins located on the surface of target cells. In the case of noradrenaline receptors are classified into two types: alpha and beta, which differ in operation speed and sometimes the sign of the effect (excitation or inhibition of the following cell).
Noradrenalinum is a major mediator of the sympathetic nervous system - the part of the brain and nerve fibers that control our internal organs during stress, physical and emotional stress, energy costs. Standing out in sympathetic synapses, norepinephrine strengthens the heart, reduces the majority of the vessels. It also dilates the bronchi (so we better breathe), inhibits gastrointestinal tract (not the time to spend resources on digestion) and so on.
It is easy to guess that the first two effects are excitatory (activation of the work of the heart muscle and vascular wall cells); the other two - the brake (relaxation of bronchial walls, stomach, intestines, cessation of secretion of digestive juices). To run such divergent changes and require different types of receptors for norepinephrine - adrenoceptors. These receptors, by the way, as effectively "respond" to the emergence of adrenaline.
Noradrenalinum and stress
One of the most important effects of the sympathetic nervous system - the activation of the inner region of the adrenal glands, their "brain matter." Eye-catching due to adrenaline (with a small amount of norepinephrine) functions as a hormone. It is important that the surface of target cells adrenoceptors are present not only in the synapse zone, but also in all other areas. As a result, the adrenaline is often a significant factor in altering the activity of a variety of organs and tissues, even than norepinephrine. Epinephrine is also able to act on these types of cells, which generally are not suitable sympathetic axons: the red blood cells, liver cells, adipose tissue, and so forth.
The effects of the activation of the adrenal medulla are not only powerful, but also lasting influence of the sympathetic nervous system. As a result, serious stress necessarily involves adrenaline component. Excessive chronic stress creates constant high concentration of adrenaline in the blood. This is wrong and can lead not only to the depletion of the body, but also impairs the health disorders of the heart, stomach, intestines.
Normally very quickly arise, but the effects are short sympathetic norepinephrine harmoniously complemented stretched endocrine action of epinephrine in time. As a result, we have a complete response in the body that occurs during stress, stress, emotions and leads him into a state of readiness of the system to the optimal response.
In the brain, neurons producing neurotransmitter as norepinephrine (noradrenergic) disposed in the locus coeruleus - a small area in the upper part of the front axle. The blue spot only a few millions of nerve cells, but their axons form a very wide network of branches. As a result of the respective synapses are found in various parts of the central nervous system (CNS) - to the end of the spinal cord, including the cerebellum and cortex in the cerebral hemispheres (and present both alpha and beta adrenergic receptors in the CNS).
Functions of noradrenaline
In the most general form of norepinephrine in the CNS function can be defined as maintenance of mental stress. At the same time it affects the overall level of brain activity, our mobility and sensory perception, emotions, needs, and memory. Let's say a few words about each of the groups of effects.
Norepinephrine is involved in establishing a certain level of waking CNS activation (due primarily braking sleep centers). As a result of the higher level of stress, so we actively. Besides, everyone knows that in the context of strong emotional feelings and thoughts, we sleep less, up to insomnia. Next norepinephrine is involved in the regulation of the brake sensory streams, which allows us to focus on those signals, which are the most important here and now. It is well known analgesic effects of norepinephrine, evident in extreme situations (stress-induced analgesia). It is known that, in a state of passion, people can not notice even serious injury or physical damage.
Furthermore, norepinephrine contributes to the control of the general level of human motor activity. The synapses generated neurons of locus coeruleus, increase mobility, step speed and jogging, cutting inhibitory neurons in the motor centers. It is this component of the action of norepinephrine leads to the fact that when strong emotions and stress, we "can not sit still."
Norepinephrine is involved in learning and memorization of information occurring in the upper (cortical) areas of the central nervous system. In this case, the activity of locus coeruleus influences centers regulated positive and negative reinforcement of the brain. Isolation of norepinephrine leads to long-term changes in synaptic properties of neural networks in the cortex and cerebellum. As a result, we firmly remember the program that led to success ( "positive reinforcement"). In parallel, the brain blocks the failed program, implementation of which led to the emergence of negative emotions ( "negative reinforcement"). Against the background of high activity of locus coeruleus people and animals learn, first of all, to avoid the trouble and remember the way out of a potentially or actually dangerous situations. Against the backdrop of a small controlled stress we learn better. However, too much stress degrades the quality of memory, and if, say, a student or a student is too afraid of the exam, it is not going to benefit the cause.
Norepinephrine is important for regulating the activity of the centers of many biological needs and motivations. These centers are located in areas of the brain, the hypothalamus and the amygdala. Influencing them, norepinephrine can cause a decrease in the level of anxiety and increased aggression manifestations. The man with the high activity of locus coeruleus often has a more pronounced choleric temperament. In dangerous situations, a pair of "Fight or flee," he often chooses the second option. His brain is often more impulsive in decision-making processes, including more prone to sudden outbursts and even inappropriate aggression.
Finally, noradrenaline strongly influences the intensity of the emotional components of behavior. This refers first of all the positive emotions that arise in an apparently stressful conditions and related concepts such as the excitement, the pleasure of risk, the joy of victory. Depending on the individual organization of the brain the significance of emotions for a specific person may be different, but sometimes very large.
Balance of Noradrenaline
Sporting events (especially extreme sports), rafting on the wild rivers and climbing, casino, roller coaster, computer games - this is not an exhaustive list of ways that mankind has come up with to enhance the release of norepinephrine and obtaining related positive emotions. Here, of course, important that the adventure has ended successfully, the match was won, and the next level of "shooter" is passed. We understand that the victim computer is virtual monster. But the adrenaline that stood out in the game, is quite real, and the person might want to get it over and over again, having thrown all the other things. So there are gambling, treatment of which in severe cases require the use of the same techniques as the treatment of this drug addiction.
In general we can say that, not only participating in the carrying out of the main flow of nerve signals can seriously norepinephrine modulate, redirect these streams, and ultimately regulate the general condition of the CNS. Knowing this, it is easy enough to imagine consequences of excessive and insufficient activity of the noradrenergic system. In the first case we may encounter with hyperactivity, aggressive and psychotic symptoms, the second - with apathy, depression (due to the shortage of positive emotions), memory impairment. In the first case, as may be necessary medication with antipsychotic properties, in the second - anti-depressants. Both of these groups of drugs can influence the activity of locus coeruleus. However, the situation is complicated by the fact that the level of emotion regulation, besides noradrenaline and other mediators are involved, especially dopamine, serotonin and endorphins.
The vast majority are used in clinical practice adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists are synthetic drugs. They are the result of work with the chemically-modified molecules of adrenaline and noradrenaline. There are, however, also natural compounds that affect the system. One example - ephedrine alkaloid gymnosperms small shrub of ephedra. Ephedrine acts as a mixed agonist of the alpha and beta-adrenergic receptors. It is able to increase blood pressure, expand the bronchi, runny nose weaken, therefore the Ephedra is widely used in folk medicine. In the case of ephedrine overdose manifest its central effects: nervous agitation, altered state of consciousness. That's why ephedrine is being considered as a narcotic drug, and ephedra - as one of the plants legally prohibited for cultivation or harvesting.
After finishing the transmission of the signal, norepinephrine slightly degraded in the extracellular environment and basically sucked back to the end of the axon (presynaptic terminals). Noradrenaline reuptake proteins is carried out by special pumps. Once in the presynaptic terminals, norepinephrine may be re-released, re-transmitting the signal. But it may decompose via the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO). Importantly, MAO and performs the above-mentioned decomposition of dopamine and serotonin. Accordingly, drugs - blockers are potent MAO antidepressants (on the background of which is better not to have sharp cheese).
Modern methods of research and medicine
Pharmacology, starting with Henry Dale, looking for molecular "master key" to the receptor proteins. These are substances similar to noradrenaline and adrenaline (agonists) or, conversely, preventing adrenaline and noradrenaline affect the target cell (receptor antagonists). Directing their effects on the heart, blood vessels, bronchi, blood pressure can be controlled (tablets) deal with allergic asthma (inhalers), treat rhinitis ( "pinch" the capillaries of the nasal cavity using special drops) and so on. Especially important to use norepinephrine receptor antagonists in the case of hypertension. Many millions of older people around the world every day are taking such drugs to protect them from heart attacks, strokes, severely prolong life and improve its quality.
Until the last couple of decades of research into the mechanisms of synaptic norepinephrine activity is mainly conducted in experimental animals. With the advent of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has become possible to see directly how the system works in humans with various activities and emotions. It is possible to investigate the role of the locus coeruleus and synapses in different parts of our brain. Volunteer-test is placed in a scanner, and he is given different tasks, tests. For example, he says, "Imagine that behind you chasing vicious dog", "Imagine that you are lying", "Imagine that next to you someone is very sick," or show emotionally charged videos and other modern methods (primarily. fMRI) allow visualization of CNS reactions in humans compare different temperament, age and so on.
Open questions
Department of Human and Animal Physiology of Moscow State University is actively exploring the sympathetic nervous system. In the human body many finely organized functions. One of the most difficult associated with the management of thousands of kilometers of blood vessels. The vessels in our various organs: the heart, the skin, intestine, muscle, brain - changing its diameter, and the tone is very different. During the active work on them acts as a norepinephrine and epinephrine, and severe stress their right balance is extremely important.
We know very little about the phylogeny - evolution and biodiversity effects of norepinephrine. Modern science, in addition to the human, is studying a very small number of model species: laboratory rats and mice, fruit flies, snail. And many hundreds of thousands and millions of other creatures living on the Earth, is almost unexplored. But it is known that bumble bee, octopus, gopher feel the world move, trained by similar brain working modules (although the very structure of the nervous system have very different). phylogeny studies allow, inter alia, to realize that we live in a world saturated with the most complex manifestations of life, and the person - not the only important and interesting thing on this planet.

 Cart
Cart