Glutamate, Acceleration Brain!
29 Dec 2016
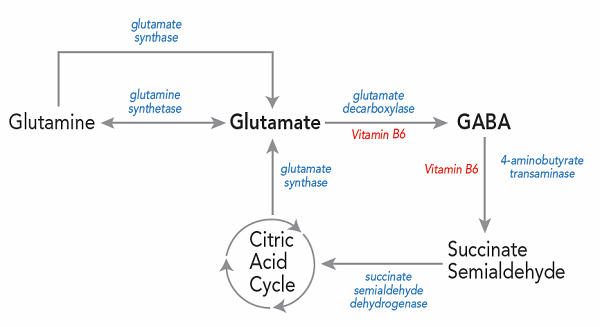
Have you ever noticed the difference between people in terms of speed of thinking? Have you ever thought about why some some consider "brakes", about the others say: "grasp on the fly." The body - is a complicated thing, and all parameters are not taken into account, perhaps, just one person is tired or dreams of something else, and we mistakenly believe that he is slow on the uptake. However, the world we know the 2 main neurotransmitter balance that is genetically shifted in one direction or another. This neurotransmitter inhibition - neurotransmitter GABA and excitation - Glutamate, they are different in direction and are still of the same material - glutamic acid. Each has its pros and cons, otherwise nature would be "cleaned up" like a broom, inefficient components of the body.
Glutamate is present in food and industrial uses. The well-known food additive - sodium glutamate, is no accident got its name, through this same neurotransmitter, it causes the brain to believe that the food is delicious. Without this addition, the food seemed to be a lot less pleasant.
How does the glutamate act?
Surface explanation - the acceleration of signal transmission between nerve cells, indirectly forcing to think and act quickly.
Nerve cells transmit signals from one to another, in the brain of such chains millions. Each chain of something is responsible, for example, to see something and react, are utilized first, retina and optic nerve, then the bark, then this chain continues until the final movement a certain part of the body. Glutamate depolarizes nerve cells like a magnet. When the magnet is directly against the metal, then one policy it will be repelled, others - attracted. Our today will be the mediator as to change the polarity of cells that all signals will speed up. You can also like Cerebramin.
Glutamate transmission speeds by acting in two ways, ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic faster metabotropic - longer. It's like 2 types of brain stimulation: fast, but not for long, or slower, but longer.
Digging even deeper, how it happens!
Recall that the mediators are allocated one neuron and interact with their receptors on the surface of the second neuron. Receptors - the second door is the nerve cell.
- 1.To activate ionotropic way it affects glutamate:
- -NMDA-receptors. Receptors that are normal, calm state "closed on the lock" Magnesium ions. But it is necessary to break into the synaptic cleft neurotransmitter glutamate as the castle and falls receptor "opens". There depolarization, back to our example with a magnet. From the 2nd neuron through the door out of calcium and potassium ions and sodium comes inside. It is the acceleration of the pulse transmission in the brain through NMDA-receptors, and it leads to synaptic plasticity, a change in power relations between nerve cells. This process is directly linked with good intelligence.
The amino acid glycine is also capable of activating these receptors, but the exact dosage are not clear.
- -AMPA-receptors. This is a very promising way to create nootropics. For details, see release on Ampakines. The bottom line is opening the 2nd door to glutamate, along with the NMDA-receptor.
- -Kainate receptors. Their role in the body poorly understood, they are less than NMDA and AMPA receptors, however, the capacity of sodium and potassium ions is comparable with the AMPA-glutamate receptor. Ie Activation of these receptors also results in faster signal transmission in the brain. That's just the speed with which depolarized postsynaptic neuron is low.
- 2.For activation path metabotropic glutamate effect on mGlu-receptors. Which are divided into three groups and 8 subtypes. Their main differences from ionotropic - different mechanism of action and a longer potential (ionotropic activated for several milliseconds, but often metabotropic from seconds to several minutes.)
- -Group 1 (mGluR1, mGluR5). It increases the activity of NMDA-receptors. When excessive activation process can excitotoxicity - neuronal death.
- -Group 2 (mGluR2, mGluR3). Lowers NMDA activity.
- -Group 3 (mGluR4, mGluR6, mGluR7, mGluR8). Lowers NMDA activity.
Pros of Glutamate:
+ increases the speed of thought
+ simpler and easier to remember something (long-term potentiation)
+ You can catch more than a short time
Cons of Glutamate:
- Impulsivity
- Anxiety / Stress
- excitotoxicity.
How to increase the production of natural glutamate?
First of all, it is necessary to obtain material - glutamic acid and glutamate from which will be created. This is mainly cheese, meat and fish. However, because this acid is formed and GABA! Initially, this proportion defines the organism. Today reliably known one way to increase glutamate - stress and cramming!
Additives to increase glutamate:
- Nootropics-Ampakines
- Cysteine
- Homocysteine
- Glutamic acid (glutamine)
- Aspartic acid
- Calcium
- Zinc in doses over 40 mg per day.
Additives to reduce glutamate:
- Any supplement with GABA activity (GABA Amminalon, Phenibut, Theanine)
- Vitamin B6.
An interesting point
Schizophrenia, autism, convulsions and ordinary is one of causes of the excessive action of glutamate in the nervous system. At high levels, it is constantly accelerates the transmission of signals, and a person is not something that begins to think quickly, his brain begins to also "overthinking" something of themselves. As it kills nerve cells and the brain dies. Therefore, it is important to understand that greater stimulation - not better! And the rate of glutamate activity all its own and is determined on the basis of their own experiences.
Bottom Line:
- Glutamate faster signaling in the brain and, in general, on the body, this is its main advantage and disadvantage.
- It is useful when you need speed, and we can sacrifice the quality.
- Runs through ionotropic and metabotropic receptors.
- Nootropics - Ampakines, calcium and zinc to increase its quantity, drugs with activity of GABA - decrease.
Good Luck

 Cart
Cart