Diabetic retinopathy
24 Jan 2019
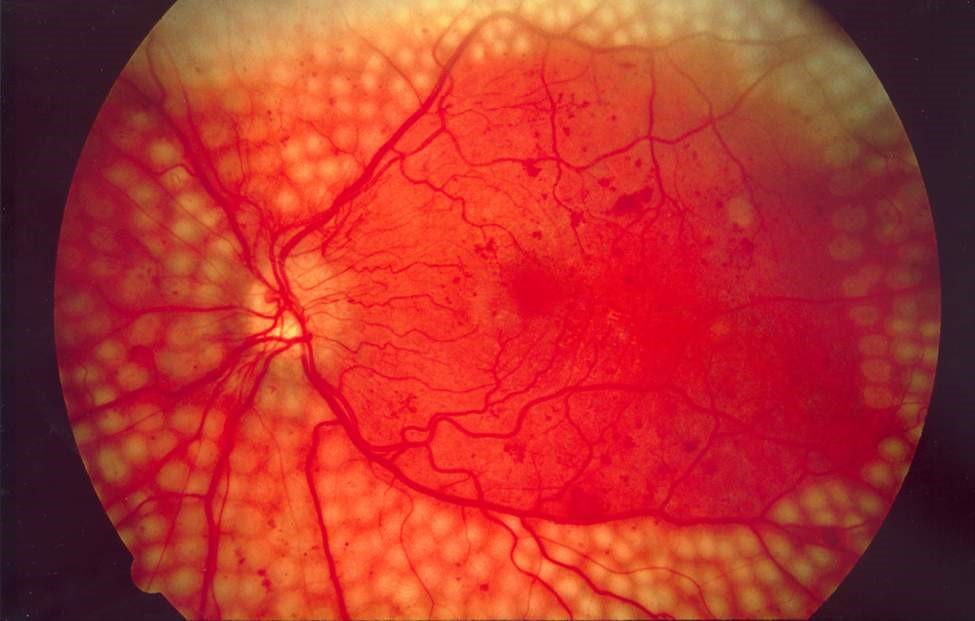
A frequent complication of diabetes is diabetic retinopathy, a specific retinal lesion. This complication develops in 70-100% of patients with diabetes mellitus and inevitably leads to impairment of visual functions, up to blindness. In the world annually about 40 thousand people suffering from diabetes mellitus become blind due to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
The frequency and progression of retinal changes depend on the effect of the so-called. objective unfavorable factors:
- duration and type of diabetes mellitus;
- compensation for diabetes mellitus and the severity of its course;
- the age of the patient;
- concomitant pathology (hypertension, atherosclerosis);
- genetic predisposition.
Diabetic retinopathy is based on microangiopathy, one of the characteristic manifestations of diabetes mellitus, which is a diffuse generalized pathological process that affects the entire microvascular system of the body.
In the case of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, patients complain of reduced vision, fog before the eyes, a desire to change glasses for reading, or do not make any complaints. With pre-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, patients may complain of a more significant and persistent decline in vision, a pronounced fog in front of the eyes, a decrease in vision both far away and close, a difficulty in reading in the usual glasses.
With proliferative diabetic retinopathy, patients complain of decreased vision until the disappearance of objective vision. Also, patients notice floating spots and strands of various sizes in front of the eyes, often dark (black, dark red) color. In addition, they note a pronounced fog, a significant loss of color perception, a lack of ability to read.
General medicines:
Anabolics: Retabolil and others.
Anticoagulants: Wessel Douay F et al.
Metabolics: Vazomag, Idrinol, Cardionate, Meldonium Organica, MILDRONATE, Actovegin etc.
Coagulants (including factors of blood coagulation), hemostatics: Etamsilat-Ferein, etc.
Correctors of cerebral circulation disorders: Vazobral, Cavinton, Sermion, etc.
Immunostimulants: Wobenzym and others.
Additional medical sources:
Angioprotectors and correctors of microcirculation: Bilobil, Bilobil intens 120, Bilobil forte, Doxie-Chem, Emoxibel, emoxipin, Venoruton, Routin, Troxerutin Vramed and others.
Biological supplements: Ophthalamine, OMEGA PREMIUM Life formula, Anthocyan Forte, Shark cartilage, Lutein complex, etc.
Vitamins and vitamin-like remedies in combinations: Vitrum Vizhn Fort, et al.
Other Metabolics: Myrtilene Forte et al.
Ophthalmic: Histochrome, Lucentis, Adgelon, and others.
Regenerants and reparants: Retinalamin, Strix, etc.

 Cart
Cart